| Dimensions | 2 × 2 × 1.25 in |
|---|---|
| Measurement | Stand is shown for scale only |
| Condition of Piece | Very good |
| Signature | Kevin Naranjo Santa Clara Pueblo |
Kevin Naranjo, cjsc3c260, Miniature bowl with sgraffito design
$375.00
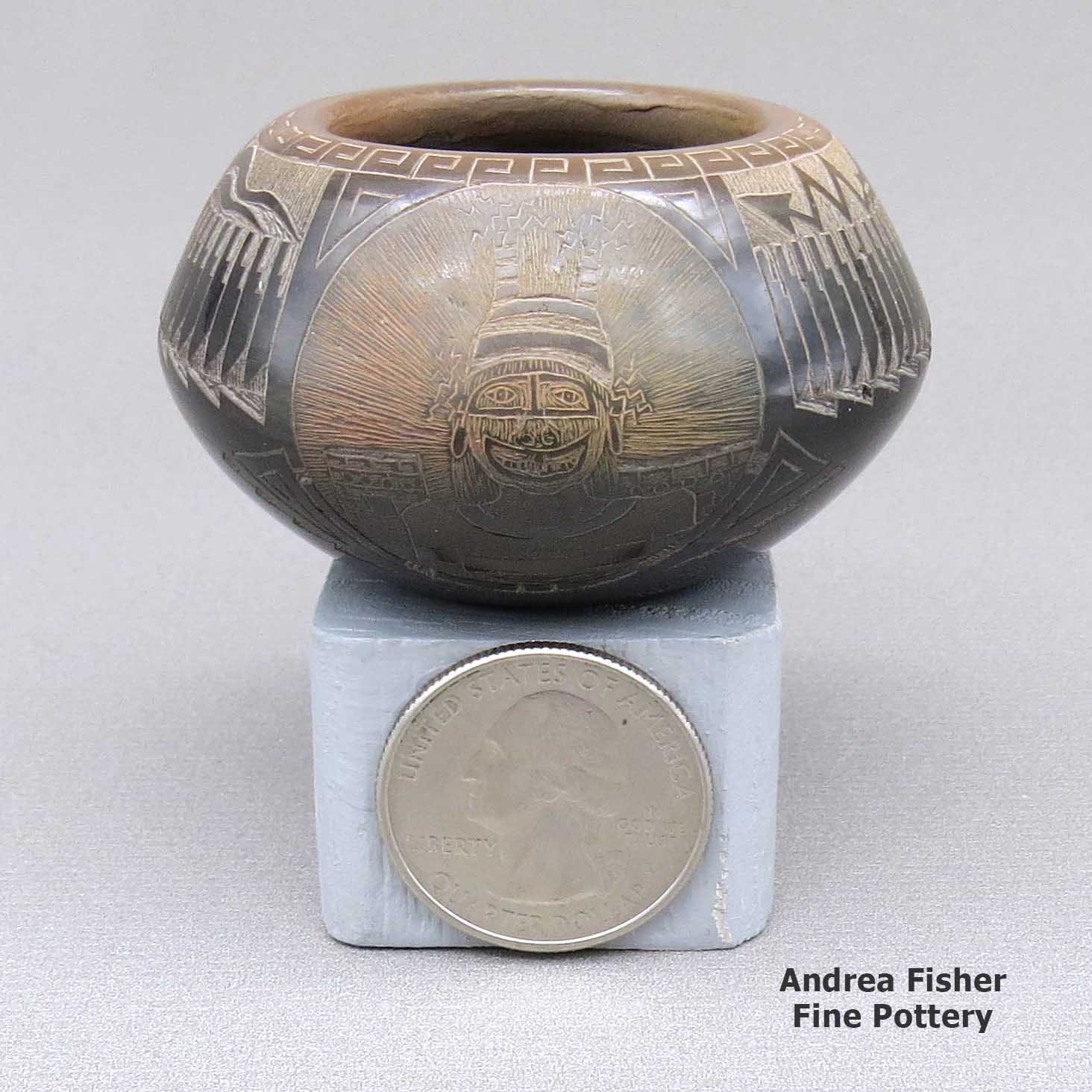
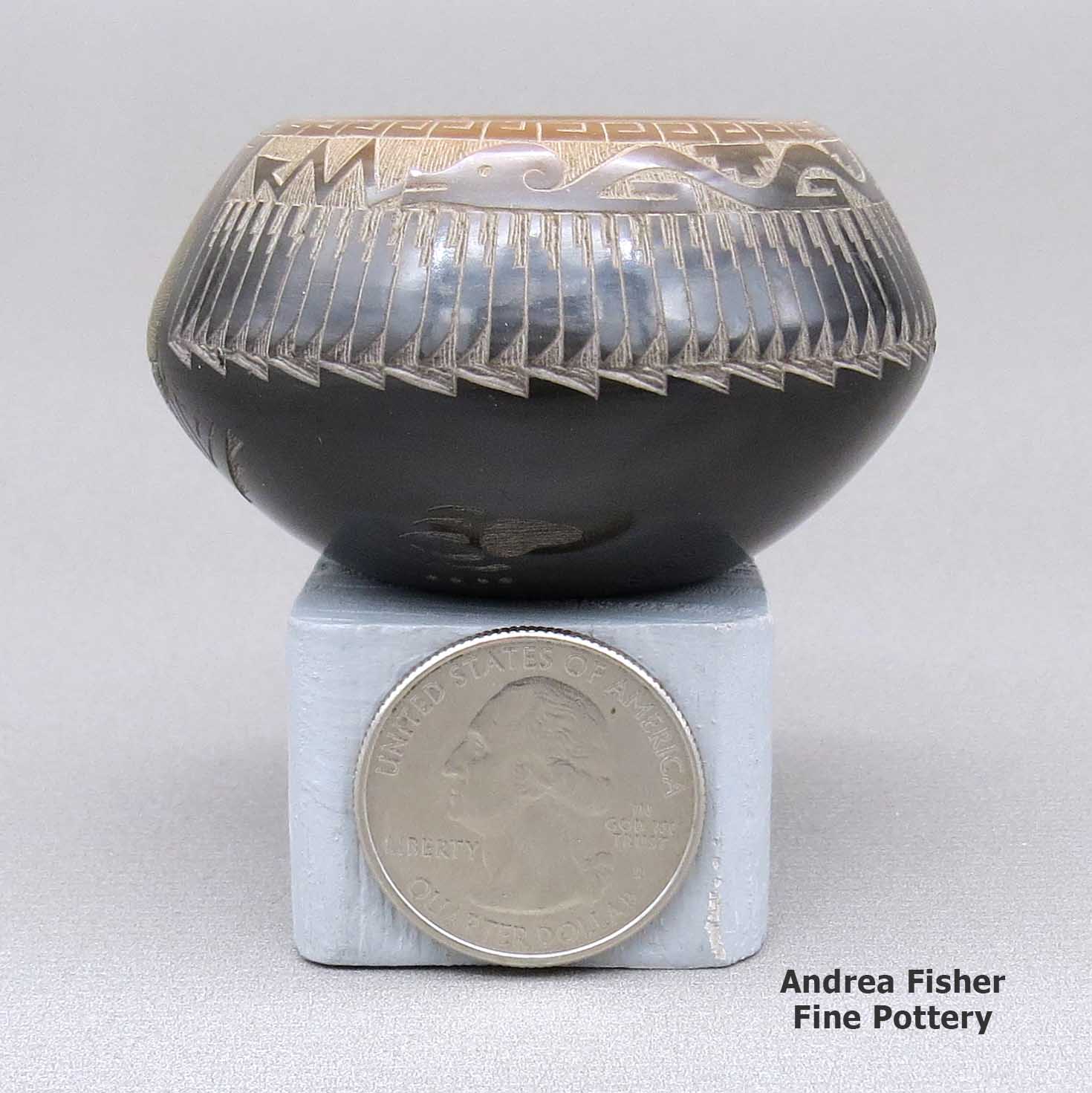
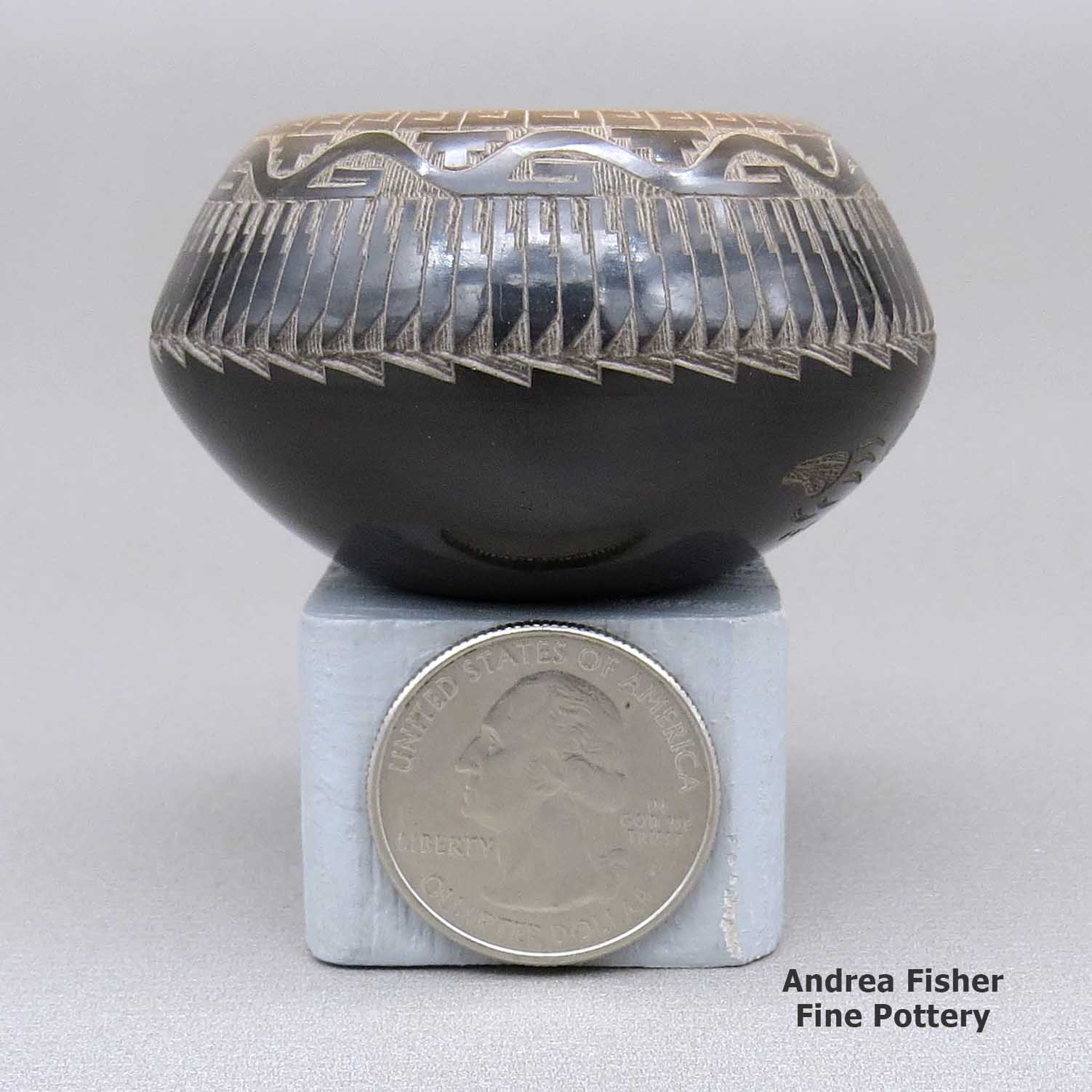
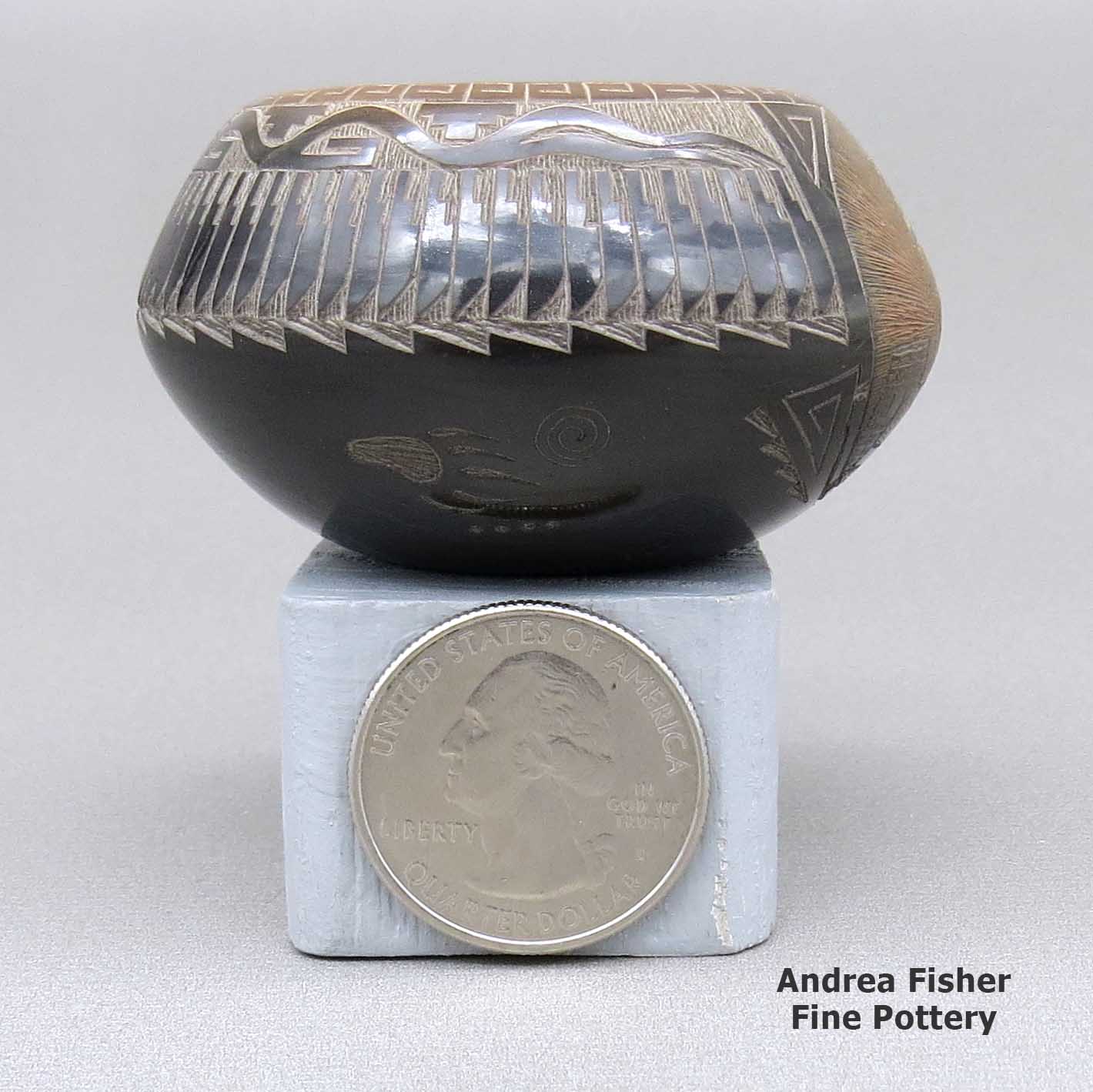
A miniature black bowl with a sienna rim and a sgraffito koshare, pueblo, avanyu, feather ring, bear paw and geometric design
In stock
- Product Info
- About the Artist
- Home Village
- Design Source
- About the Shape
- About the Design
- Family Tree
Brand
Naranjo, Kevin
 Born in 1972 at Santa Clara Pueblo, Kevin Naranjo was given a Tewa name meaning Turquoise Mountain. He says he was inspired to learn the ancient tradition of hand coiling pottery by the time he was four. That inspiration came from his family and his love of nature.
Born in 1972 at Santa Clara Pueblo, Kevin Naranjo was given a Tewa name meaning Turquoise Mountain. He says he was inspired to learn the ancient tradition of hand coiling pottery by the time he was four. That inspiration came from his family and his love of nature.Kevin was born into a family of famous potters, including Luther Gutierrez (his great-grandfather), Dolores Curran (a maternal aunt) and Geri Naranjo (his mother). Geri is renowned for her miniature sgraffito (fine line incised) pottery, the traditional methods of which she taught to both Kevin and his sister, Monica Naranjo.
Specializing in hand coiled black and sienna sgraffito pottery, Kevin gathers his clay from sacred grounds within Santa Clara Pueblo. He digs and prepares the clay, hand-coils and shapes his forms, then lets them dry for a few days. Then he stone polishes the surfaces and ground fires his pottery using an oxygen-reduction process to make the black canvas for his designs. After firing, he etches the pot to create wonderful scenes of wildlife that live in the area of his home at Santa Clara.
The first piece he made as a child was a dinosaur. He remembers it well: it sparked an interest in molding animal figurines. That first inspiration and practice evolved until now his pottery embodies beautiful symmetry, graceful lines and finely executed sgraffito designs like the avanyu (water serpent), kiva steps and the feather pattern. Additional figures such as bears, eagles, bighorn sheep, deer and elk are incorporated into backgrounds of pueblo ruins and mountain views.
For several years, Kevin collaborated with Tricia Pena from San Ildefonso Pueblo. Her grandfather, the late Encarnacion Pena, was a member of the original San Ildefonso School of Painters.
Kevin has consistently earned awards for his sgraffito and miniature pottery since starting to compete in 1994. He's most proud of the First Place and Best of Division ribbons he earned in the Miniature Sgraffito category at the 2004 Santa Fe Indian Market. He'd earned his first First Place ribbon at the 2000 Santa Fe Indian Market with a burnished black Miniature Sgraffito piece.
A Short History of Santa Clara Pueblo
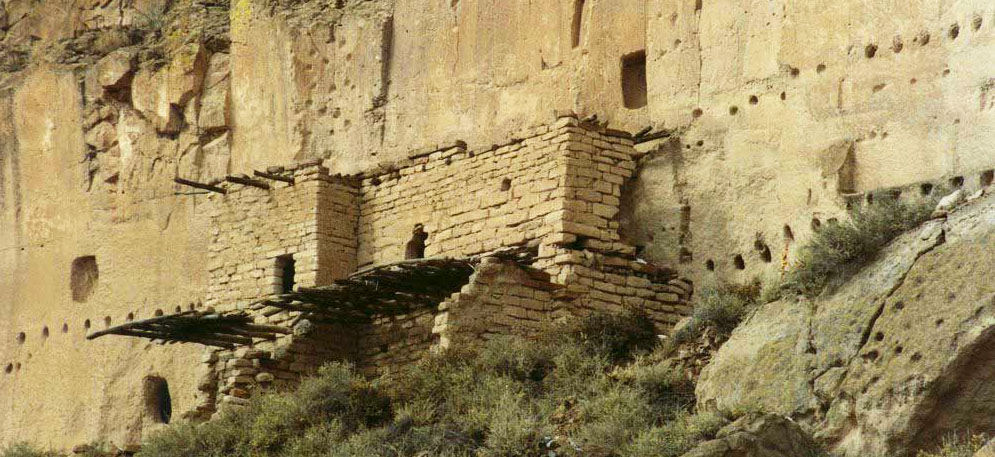

Santa Clara Pueblo straddles the Rio Grande about 25 miles north of Santa Fe. Of all the pueblos, Santa Clara has the largest number of potters.
The ancestral roots of the Santa Clara people have been traced to ancient pueblos in the Mesa Verde region in southwestern Colorado. When the weather in that area began to get dry between about 1100 and 1300 CE, some of the people migrated to the Chama River Valley and constructed Poshuouinge (about 3 miles south of what is now Abiquiu on the edge of the mesa above the Chama River). Eventually reaching two and three stories high with up to 700 rooms on the ground floor, Poshuouinge was inhabited from about 1375 CE to about 1475 CE.
Drought then again forced the people to move. One group of the people went to the area of Puyé (along Santa Clara Canyon, cut into the eastern slopes of the Pajarito Plateau of the Jemez Mountains). Another group went south of there to what we now call Tsankawi. A third group went a bit to the north, following the Rio Chama down to where it met the Rio Grande and founded Ohkay Owingeh on the northwest side of that confluence.
Beginning around 1580, another drought forced the residents of the Puyé area to relocate closer to the Rio Grande. There, near the point where Santa Clara Creek merged into the Rio Grande, they founded what we now know as Santa Clara Pueblo. Ohkay Owingeh was to the north on the other side of the Rio Chama. That same dry spell forced the people down the hill from Tsankawi to the Rio Grande where they founded San Ildefonso Pueblo to the south of Santa Clara, on the other side of Black Mesa.
In 1598 Spanish colonists from nearby Yunqué (the seat of Spanish government near the renamed "San Juan de los Caballeros" Pueblo) brought the first missionaries to Santa Clara. That led to the first mission church being built around 1622. However, the Santa Clarans chafed under the weight of Spanish rule like the other pueblos did and were in the forefront of the Pueblo Revolt of 1680. One pueblo resident, a mixed black and Tewa man named Domingo Naranjo, was one of the rebellion's ringleaders.
When Don Diego de Vargas came back to the area in 1694, he found most of the Santa Clarans were set up on top of nearby Black Mesa (with the people of San Ildefonso, Pojoaque, Tesuque and Nambé). An extended siege didn't subdue them but eventually, the two sides negotiated a treaty and the people returned to their pueblos. However, successive invasions and occupations by northern Europeans took their toll on the pueblos over the next 250 years. The Spanish flu pandemic in 1918 almost wiped them out.
Today, Santa Clara Pueblo is home to as many as 2,600 people and they comprise probably the largest per capita number of artists of any North American tribe (estimates of the number of potters run as high as 1-in-4 residents).
For more info:Pueblos of the Rio Grande, Daniel Gibson, ISBN-13:978-1-887896-26-9, Rio Nuevo Publishers, 2001
Upper photo courtesy of Einar Kvaran, Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported License
Tewa Design Sources
The Northern Tewa people are mostly from the villages of Ohkay Owingeh, Santa Clara, San Ildefonso, Pojoaque, Nambé and Tesuque. The Hopi-Tewa of Arizona are descendants of the Southern Tewa. The Tewa share a common heritage from back in the 1200s CE, when their ancestors lived in the canyons and valleys west of Mesa Verde. When the Great Drought hit (around 1276 CE), they were already on the move because of other recent bad weather events. The kachina cult was developing around the same time and however it worked out, never took hold among the Tewa. The Tewas did incorporate the Medicine and Sacred Clown societies into their religious activities. Archaeologists have traced their tracks east from the Four Corners to the South San Juan Mountains, where they turned south and first built homes in New Mexico around Ojo Caliente. From there, they spread further south into the valley of the Rio Chama and then spread out there for a hundred years.
As more and more Dineh and Apaches came into the area in the 1400s, the Tewa moved downstream along the Chama. Some of them moved up onto the Pajarito Plateau while others sorted out into small villages on the east side of the Rio Grande. Shortly some of them came to the southern edge of the Santa Fe River Basin and found the Galisteo Creek Basin on the other side populated by Eastern Keres people. It was the same when they came to the mouth of the Santa Fe River at the Rio Grande: further south along the river was populated by other Eastern Keres people. And just upstream across the Rio Grande was the outlet of Frijoles Canyon, home of many Eastern Keres people in the 1400s and 1500s.
There were indigenous Tanoan people already living throughout the Rio Grande area and the two groups merged reasonably well. Somewhere in this time period, sodalities came into being: the Summer People and the Winter People. Some archaeologists believe the incoming Tewa became the Summer People and the Tanoans became the Winter People, based on the fact the incoming Tewas brought new seeds, new agricultural and ceramic technology, new dances and new religion. When the Spanish first arrived in the area around 1540 CE, the Tewa Basin was well occupied by the merged Tewa/Tano people. Those Tanoans who preferred not to merge built separate pueblos for themselves in more marginal areas in the Santa Fe and Galisteo River basins. Depopulation began after the Spanish left and didn't take their various diseases with them. It was after Don Diego de Vargas arrived in 1598 that the survivors were separated into their separate villages and restricted to those.
The Northern Tewa
The Northern Tewa design pallette contains a number of motifs common to many puebloan societies: hummingbirds, turtles, tadpoles, quails, owls, deer, hands, hoof prints, bird tracks and more. It's easy to see how many evolved from designs from the Flower World Complex of central Mexico. The Santa Clara and Nambé avanyu is a winding serpent with usually, one or three feathers on the top of its head. The San Ildefonso avanyu usually has a three- or five-pronged plume on its head. The avanyu itself is evolved from images of Quetzalcoatl. While the avanyu is the protective spirit of water and springs it also represents what happens when there's a heavy rain in the desert: flash floods that can wipe out whole villages.
Most San Ildefonso potters paint their decorations, only a few work with sgraffito decorations and a few work with inlaid stones and heishi beads. At Santa Clara, potters carve, scratch and paint their pieces, then sometimes reheat them with a blowtorch and mount stones on them... almost anything goes. The design palette is traditional to trend-setting contemporary, although the subject matter is usually the avanyu, or hummingbirds, turtles, quails, fish, deer, bear paws and bear claws, etc.
Because they had easy access to micaceous clay, the people of Nambé and Ohkay Owingeh built a brisk business in making micaceous pots and cookware, similarly to the people of Taos and Picuris at the time. More recently, Lonnie Vigil and Robert Vigil have produced micaceous pottery at Nambé while Clarence Cruz has been producing micaceous cookware and utensils at Ohkay Owingeh.
The people of Ohkay Owingeh decided to start over after essentially losing their pottery tradition in the 1800s. They never stopped making utilitarian pottery but even that declined in the late 1800s. In the 1920s, when it was decided they would work to revive a purely Ohkay Owingeh tradition, they settled on the designs found on some prehistoric pottery that had been found while digging in an old Tewa pueblo on Ohkay Owingeh land. The pottery was dated to the few decades before the Spanish arrived, hence: pre-contact and innocent of European influence. Their definition of Potsuwi'i pottery is very specific as to the colors and textures of the clay used and the designs carved, scratched or painted on them. Many of the design patterns are reflective of rock art from a thousand years ago.
The Southern Tewa
The Santa Fe Basin is where the Southern Tewa settled. They seem to have followed the idea that "further south is a better life," and they kept going south until they came up against other relatively entrenched people (migrants spreading out from Santo Domingo into the Galisteo Creek Basin). The Santa Fe Basin showed signs of having been occupied by the Tanoan people off-and-on over the centuries. It was a marginal landscape for farming but it was up against the Cerrillos Hills where they found turquoise, silver and lead ore. The turquoise trade was very profitable for some but the lead ore made possible different design techniques to use on fired pottery. The potters of the village did well producing lead-glazed pottery (not sealed, glazed only where the lead paint was applied and then ran in the heat of the fire).
In 1692, when the Spanish arrived in full force to reconquer northern New Mexico, most of the Tewa people in Tewa Basin gathered atop Black Mesa, a volcanic plug that sits between Santa Clara and San Ildefonso Pueblos. They stayed up there for months, almost impervious to Spanish attack. Eventually, though, they made a deal with the Spanish and returned to their various pueblos.
Shortly after that, the Spanish issued an order limiting access to the lead mines at the Cerrillos Hills to Spanish citizens only and, with that, the Southern Tewa lost their last possibility for remaining in a parched landscape. Because of the boundaries imposed by the Spanish, they all ran north in the night to the area of Chimayo. That didn't work out quickly, so they moved to the area of Santa Clara, again during the night. That didn't work out either as they were challenged by a Spanish priest and they killed him. From there they moved quickly to the area of Zuni, then up to First Mesa where they made a deal with the people of Walpi and were shortly living in their own village near the base of First Mesa. Over the centuries they came to be known as the Hopi-Tewa. In that same time period many of the religious aspects of Hopi society have made their way into Hopi-Tewa society. The Hopi-Tewa design pallette consists mostly of designs revived from potsherds found around the ancient pueblos of Awatovi, Sikyátki, Payupki and Kawaika'a, all of which are in the vicinity of the Hopi mesas.
About Bowls
The bowl is a basic utilitarian shape, a round container more wide than deep with a rim that is easy to pour or sip from without spilling the contents. A jar, on the other hand, tends to be more tall and less wide with a smaller opening. That makes the jar better for cooking or storage than for eating from. Among the Ancestral Puebloans both shapes were among their most common forms of pottery.
Most folks ate their meals as a broth with beans, squash, corn, whatever else might be in season and whatever meat was available. The whole village (or maybe just the family) might cook in common in a large ceramic jar, then serve the people in their individual bowls.
Bowls were such a central part of life back then that the people of the Classic Mimbres society even buried their dead with their individual bowls placed over their faces, with a "kill hole" in the bottom to let the spirit escape. Those bowls were almost always decorated on the interior (mostly black-on-white, color came into use a couple generations before the collapse of their society and abandonment of the area). They were seldom decorated on the exterior.
It has been conjectured that when the great migrations of the 11th, 12th, 13th and 14th centuries were happening, old societal structures had to change and communal feasting grew as a means to meet, greet, mingle with and merge newly arrived immigrants into an already established village. That process called for larger cooking vessels, larger serving vessels and larger eating bowls. It also brought about a convergence of techniques, styles, decorations and design palettes as the people in each locality adapted. Or didn't: the people in the Gallina Highlands were notorious for their refusal to adapt and modernize for several hundred years. They even enforced a No Man's Land between their territory and that of the Great Houses of Chaco Canyon, killing any and all foreign intruders. Eventually, they seem to have merged with the Towa as those people migrated from the Four Corners area to the southern Jemez Mountains.
Traditional bowls lost that societal importance when mass-produced cookware and dishware appeared. But, like most other Native American pottery in the last 150 years, market forces caused them to morph into artwork.
Bowls also have other uses. The Zias and the Santo Domingos are known for their large dough bowls, serving bowls, hair-washing bowls and smaller chili bowls. Historically, these utilitarian bowls have been decorated on their exteriors. More recently, they've been getting decorated on the interior, too.
The bowl has also morphed into other forms, like Marilyn Ray's Friendship Bowls with children, puppies, birds, lizards and turtles playing on and in them. Or Betty Manygoats' bowls encrusted with appliqués of horned toads or Reynaldo Quezada's large, glossy black corrugated bowls with custom ceramic black stands.
When it comes to low-shouldered but wide circumference ceramic pieces (such as many Sikyátki-Revival and Hawikuh-Revival pieces are), are those jars or bowls? Conjecture is that the shape allows two hands to hold the piece securely by the solid body while tipping it up to sip or eat from the narrower opening. That narrower opening, though, is what makes it a jar. The decorations on it indicate that it is more likely a serving vessel than a cooking vessel.
This is where our hindsight gets fuzzy. In the days of Sikyátki, those potters used lignite coal to fire their pieces. That coal made a hotter fire than wood or manure (which wasn't available until the Spanish brought it). That hotter fire required different formulations of temper-to-clay and mineral paints. Those pieces were perhaps more solid and liquid resistant than most modern Hopi pottery is: many Sikyátki pieces survived intact after being slowly buried in the sand and exposed to the desert elements for hundreds of years. Many others were broken but were relatively easy to reassemble as their constituent pieces were found all in one spot and they survived the elements. Today's pottery, made the traditional way, wouldn't survive like that. But that ancient pottery might have been solid enough to be used for cooking purposes, back in the day.
About Sgraffito Designs
"Sgraffito" is from the Italian, meaning "to scratch." It's a technique wherein designs are scratched into the surface of a piece of pottery, generally with the use of a needle, dental tool or other sharp object. Also usually, the surface of the piece has been slipped with one color of clay and scratching through it reveals the design in a different color of clay. Some potters will slip a piece with layers of various colors of clay and the depth of their etching gives a color depth to their designs. Some will fire their pieces first, using the firing process to produce different effects in the clay. When they etch them after, the different depths they etch to also lend a color depth to their designs.
The sgraffito technique has been widely used in Europe for centuries but only came to the pueblos in the late 1960s. Even then, it's only really been developed at Jemez, Santa Clara, San Ildefonso and Ohkay Owingeh. At Santa Clara, Joseph Lonewolf and his father, Camilio Tafoya, and sister, Grace Medicine Flower, have been credited as being among the first to develop sgraffito. Corn Moquino was there, too, in those early days. At San Ildefonso, Juan Tafoya and Barbara Gonzales were among the first. At Ohkay Owingeh, Alvin Curran and Tom Tapia were among the first. Juanita Fragua was among the earliest at Jemez.
In Mata Ortiz, virtually anything goes and sgraffito has been widely used since the early 1970s. Again, some potters scratch their designs before firing, some after. Some scratch to add textured designs to an otherwise same-colored surface. Some carve and scratch and then fire. Some carve, paint and fire, then scratch... The tools they use vary from dental picks and exacto knives to nails, file handles and sharpened bicycle spokes.
Marie Suazo Family Tree - Santa Clara Pueblo
Disclaimer: This "family tree" is a best effort on our part to determine who the potters are in this family and arrange them in a generational order. The general information available is questionable so we have tried to show each of these diagrams to living members of each family to get their input and approval, too. This diagram is subject to change should we get better info.
- Marie Suazo
- Ursulita Naranjo and Alfred Naranjo
- Dolores Curran & Alvin Curran (San Juan) (1953-1999)
- Geri Naranjo
- Kevin Naranjo (1972-)
- Monica Naranjo (Romero)
- Alfred Ervin Naranjo & Jennifer Naranjo (Sisneros)
- Alfred Naranjo (1980-)
- Dolores Curran & Alvin Curran (San Juan) (1953-1999)