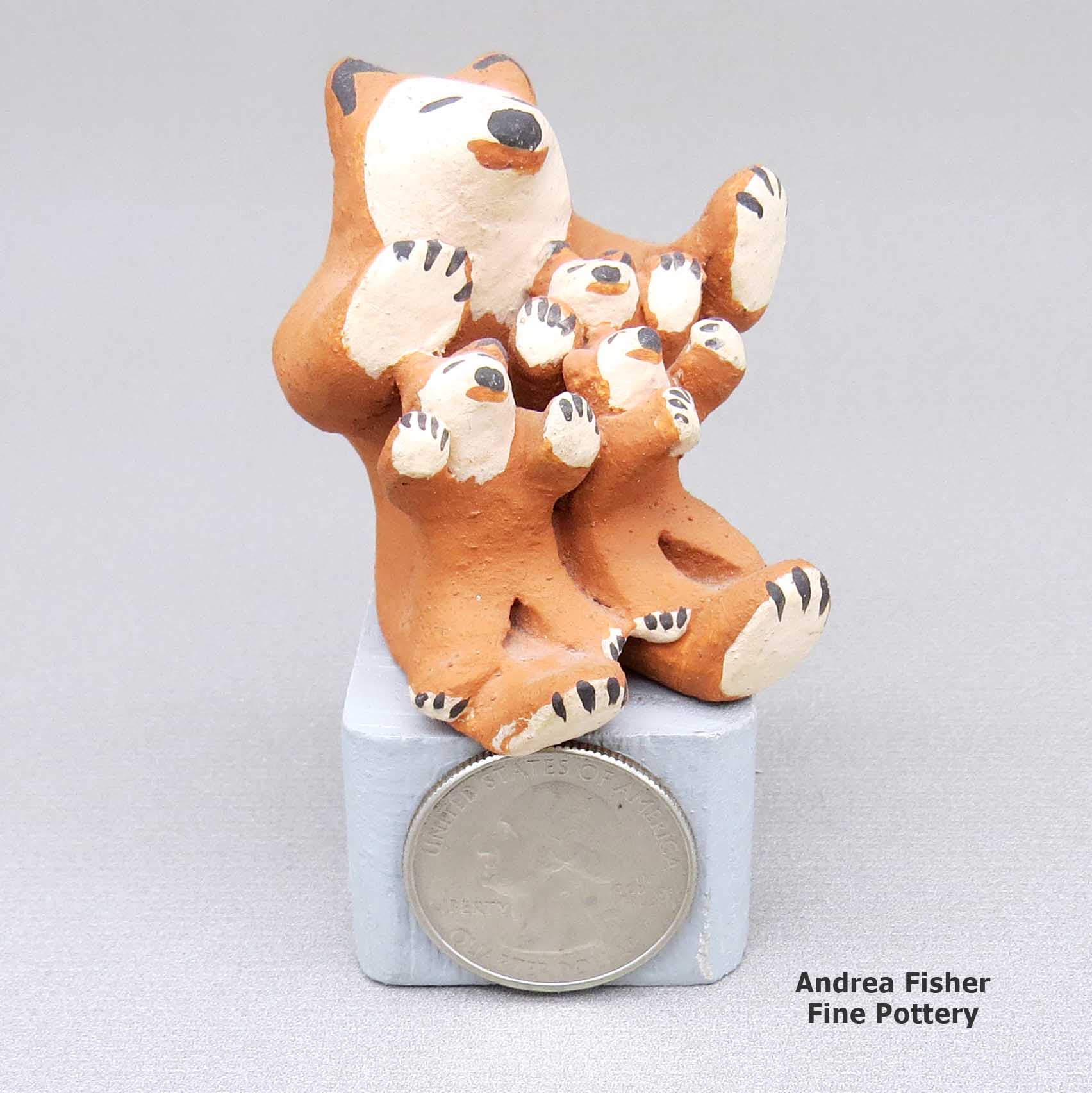
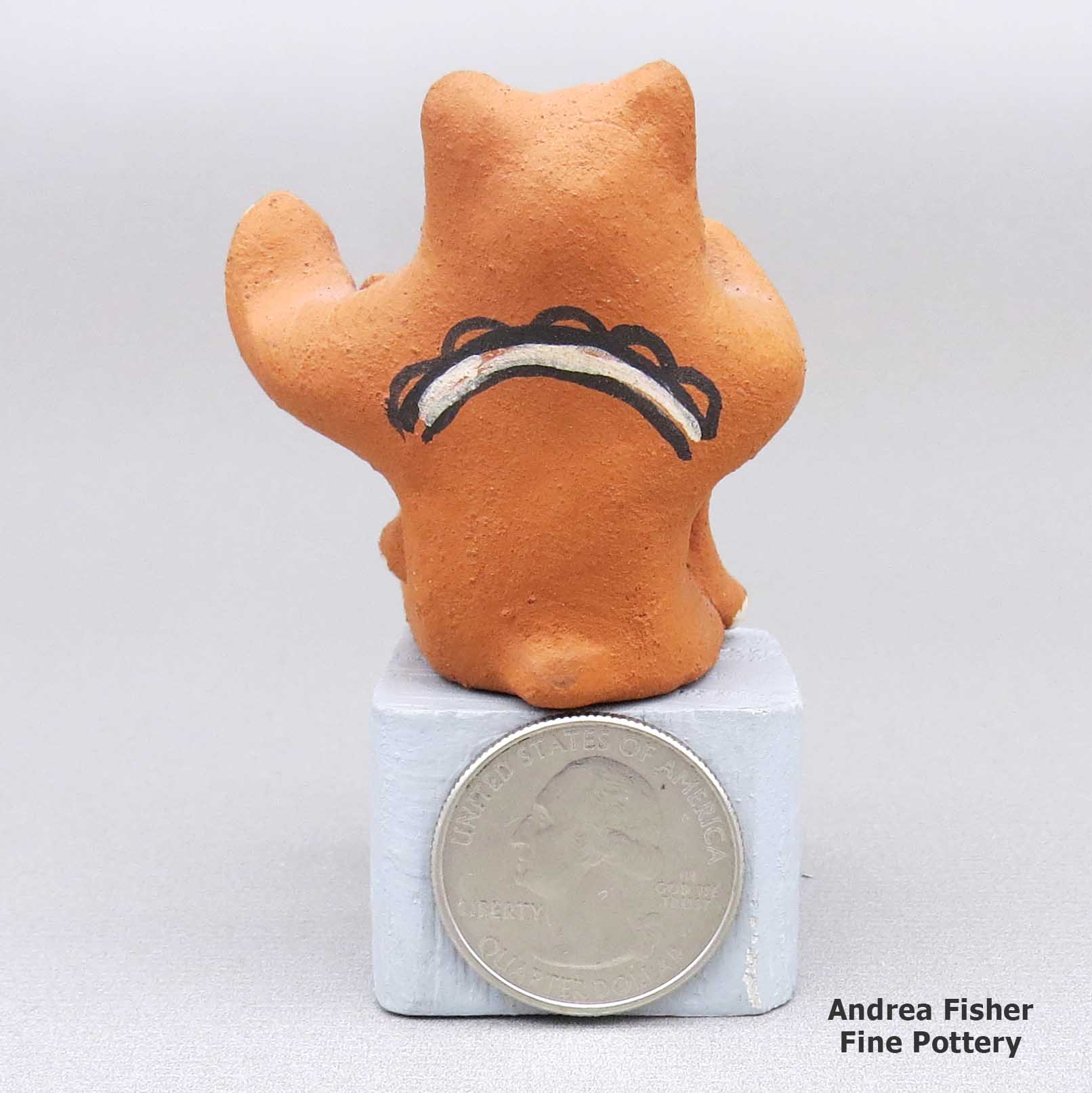
| Dimensions | 1.75 × 1.75 × 1.75 in |
|---|---|
| Measurement | Stand is shown for scale only |
| Condition of Piece | Very good, normal wear |
| Signature | Marie P. Romero |
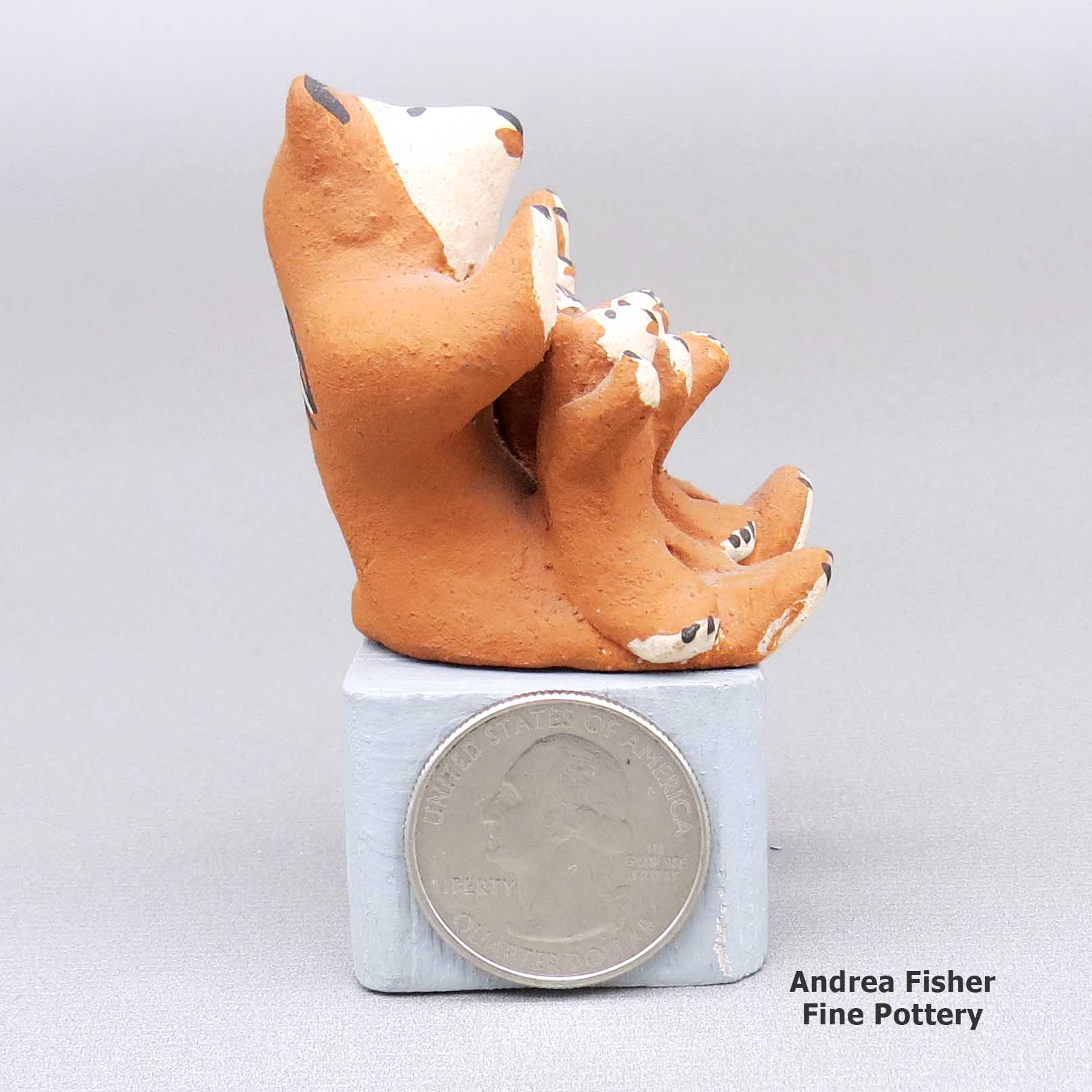
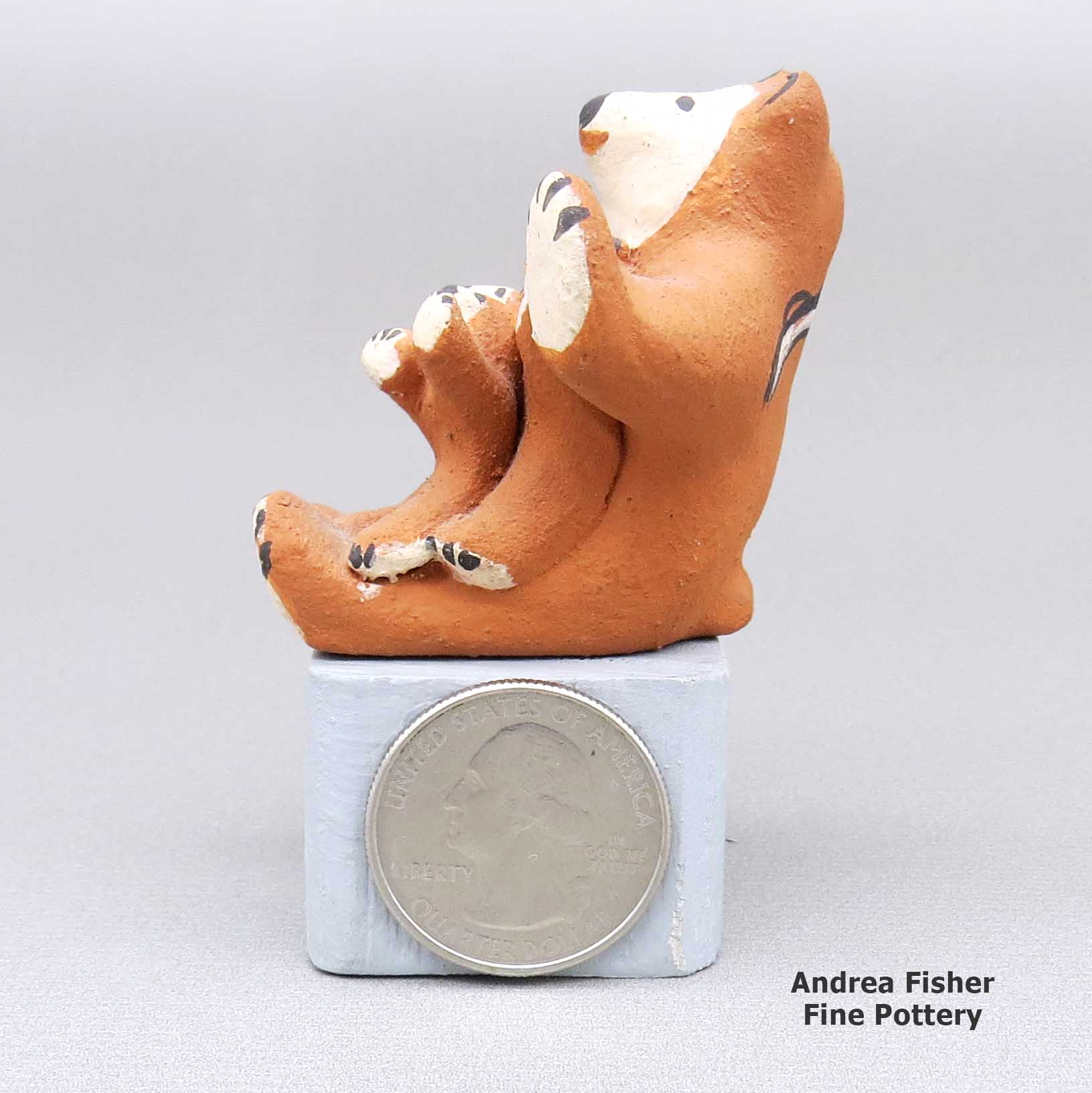
Marie Romero, lcco3b105, Miniature bear storyteller with three cubs
$110.00
Miniature polychrome bear storyteller with three cubs
In stock
Brand
Romero, Marie
Marie G. Romero was born into the Corn Clan at Jemez Pueblo in July 1927. Her parents were Joe and Persingula Gachupin. Leonora G. Fragua was her sister. They both grew up learning how to make pottery through watching and working with their mother.
Marie was making pottery and selling it early in life. She made pottery for more than 50 years. She made the usual Jemez matte polychrome and polished red jars, bowls, canteens and wedding vases but she also made storytellers, miniature kivas, nativities, old-lady-in-the-shoe scenes and hunter figures.
Between 1976 and 1999 Marie participated in juried competitions at the Santa Fe Indian Market, the Heard Museum Guild Indian Arts Fair & Market, the Gallup InterTribal Ceremonial, the Eight Northern Pueblos Arts & Crafts Show and the New Mexico State Fair. She won many First, Second and Third Place ribbons in those years.
Marie is the mother of Laura Gachupin and Maxine Toya, grandmother of Dominique Toya, Camilla Toya, Benina Foley and Gordon Foley.
A Short History of Jemez Pueblo

As the drought in the Four Corners region deepened in the late 1200s, several clans of Towa-speaking people migrated southeastward, across the Upper San Juan River into the Gallina Highlands, then over the hill to the Canyon de San Diego area in the southern Jemez mountains. Other clans of Towa-speaking people migrated southwest and settled in the Jeddito Wash area in northeastern Arizona, below Antelope Mesa and southeast of Hopi First Mesa. The large migrations out of the Four Corners area began around 1250 and the area was almost entirely depopulated by 1300. The Towa-speakers who went southeast were pretty much settled by about 1350.
Archaeologist Jesse Walter Fewkes argues that pot sherds found in the vicinity of the ruin at Sikyátki (near the foot of Hopi First Mesa) speak to the strong influence of earlier Towa-speaking potters on what became "Sikyátki Polychrome" pottery (Sikyátki was a village at the foot of First Mesa, destroyed by other Hopis around 1625). Fewkes maintained that Sikyátki Polychrome pottery was the finest ceramic ware ever made in prehistoric North America.
Francisco de Coronado and his men arrived in the Jemez Mountains of Nuevo Mexico in 1539. By then the Jemez people had built several large masonry villages among the canyons and on some high ridges in the area. Their population was estimated at about 30,000 and they were among the largest and most powerful tribes in northern New Mexico. Some of their pueblos reached five stories high and contained as many as 3,000 rooms.

Because of the nature of the landscape they inhabited, agriculture was hard. The Jemez had always been travelers and traders. Their people had traded goods all over the Southwest and northern Mexico for generations. In those days they also made a lot of pottery and trading pottery with Zia and Santa Ana Pueblos for food was a brisk business.
The arrival of the Spanish was disastrous for the Jemez and they resisted the Spanish with all their might. That led to many atrocities against the tribe until they rose up in the Pueblo Revolt of 1680 and helped evict the Spanish from northern New Mexico. With the Spanish gone, the Jemez destroyed much of what they had built on Jemez land. Then they concentrated on preparing themselves for the eventual return of the hated priests and the Spanish military.
The Spanish returned in 1692 and their efforts to retake northern New Mexico bogged down as the Jemez fought them doggedly for four years. In 1696 many Jemez came together, killed a Franciscan missionary and then fled to join their distant relatives in the Jeddito Wash area in northeastern Arizona. They remained at Jeddito Wash for several years before returning to the Jemez Mountains.
It was around that time that the Hopi themselves destroyed Awatovi, the largest pueblo in the Hopi area (many of the people of Awatovi also spoke Towa). A Spanish missionary with a few soldiers had appeared at Awatovi in 1696 and forced the rebuilding of the mission. He also started getting people into the church. The leader of Awatovi went to the other Hopi pueblos and told their leaders that his people had strayed too far: they must be destroyed to cleanse the Earth of their sins. In the winter of 1700-1701, men from Walpi, Oraibi and a couple other pueblos invaded Awatovi while the men were in their kivas. The invaders pulled the ladders out of the kivas, poured baskets of hot red chile peppers and burning pine pitch down, then killed almost everyone. When the frenzy was over they burned the pueblo down and salted the earth around it so it would never be reoccupied.
On their return to the Jemez Mountains around 1700, the Jemez people built the pueblo they now live in (Walatowa: The Place) and made peace with the Spanish authorities. Even today, there are still strong ties between the Jemez and their cousins on Dineh territory at Jeddito.
East of what is now Santa Fe is where the ruins of Pecos Pueblo (more properly known as Cicuyé) are found. Cicuyé was a large pueblo housing up to 2,000 people at its height. The people of Cicuyé were the easternmost speakers of the Towa language in the Southwest. After the Pueblo Revolt, the Pecos area fell on increasingly hard times (constant Apache and Comanche raids, European diseases, increasing drought). The pueblo was finally abandoned in 1838 when the last 17 residents relocated to Jemez. The Governor of Jemez welcomed them and allowed them to retain many of their Pecos tribal offices (governorship and all). Members of former Pecos families still return to the site of Cicuyé every year to perform religious ceremonies in honor of their ancestors.


For more info:
Pueblos of the Rio Grande, Daniel Gibson, ISBN-13:978-1-887896-26-0, Rio Nuevo Publishers, 2001
Prehistoric Hopi Pottery Designs, Jesse Walter Fewkes, ISBN-0-486-22959-9, Dover Publications, Inc., 1973
Photos are our own. All rights reserved.
About Figures and Figurines
Generally, "Figure" denotes a real or mythic creature, like an owl or human or katsina or Corn Maiden. Whether form or decoration, all Puebloan pottery figures are meant to invoke particular spiritual essences. That's why "effigy" is used almost as often as "figure" to denote these pieces.
Among most Puebloans, the figure of an owl, for example, signifies all the physical and spiritual aspects attributed to the owl. It's a form of prayer to the spirit of "Owl" and the appropriately decorated physical form is meant to make that spirit manifest. However, to the Zuni people an owl is a good omen and to the Tewa people, an owl is a bad omen. Some potters at Santa Clara have made owls anyway, they just shaped and decorated them to reflect that "badness."
That explanation may make more sense in the case of the Corn Maiden as she is a mythic entity whose existence revolves around the most ubiquitous food staple in the Puebloan world: corn (maize). All representations of the Corn Maiden are meant to invoke her benevolence and abundance for their people. Because of her mythical/spiritual nature, different pueblos have slightly different physical forms for her but they all incorporate the basic form of a female human face on an ear of corn.
The potters of Tesuque turned out thousands of muna figures (also known as rain gods)for several decades, until they virutally burned out their pottery tradition. These muna had very specific shapes but were decorated with everything from micaceous slips to incised lines to polychrome geometric designs to poster paints. They were also made purely for domestic American consumption, sometimes delivered by the barrel to be used as prizes and giveaways.
The Storyteller is another figure based on Puebloan tradition: a tribal elder singing the stories of the tribe's oral history to the children. The original was based on the traditional cultural story: a grandfather singing his part of the story in his native language so the children learn both the language and their identity against the backdrop of that history. Shortly, the storyteller form was duplicated in several other pueblos, each pueblo's potters adapting the form to their local situation. In some places, the grandmother became the primary sex of their storytellers. At Jemez, that responsibility was shared between grandmothers and grandfathers. Then some potters in search of new niches in the marketplace branched into making "spirit figure" storytellers, like eagles, ravens, hummingbirds, cats and dogs. Some Zuni potters have made storyteller owls.
Similar to the Storyteller is the Story Time: a set of separate children displayed around a larger central singing figure.
The Nativity set (also known as nacimiento) is a set of figures based on the intersection of Puebloan mythologies and stories they heard from Christian missionaries. Those potters who make them also tend to favor dress, shapes and designs that reflect their own heritage(s). The first few nativities made at Tesuque Pueblo were decorated with Spanish colonial costumes but that soon changed and every nativity made since has a distinct blend of Native American and Christian, with no other reference to colonialism. The "Singing Angel" (a single standing figure with outstretched wings and hands clasped together in prayer) and "Flight to Egypt" (usually depicting Mary with a baby Jesus on the back of a donkey and a standing Joseph nearby holding the rein) are similar mixes of tribal and Christian figures. The miniature nativities made by Santa Clara/Dineh artist Linda Askan clearly show Dineh religious influence in the headresses worn by Joseph, the angel and the three wise men. At the same time, the Dineh Folk Art nativities made by Jonathan Chee are based on the realities of daily Dineh life: the three wise men wear wide-brim hats and blue jeans, and bring gifts of salt and 50-pound bags of flour.
Pueblo and Dineh artists also make a full zoo of domesticated, farm and wild animal figures: horses, donkeys, cows, chickens, pigs, sheep, turkeys, giraffes, elephants, dogs, cats, mermaids, women-dressed-up-and-taking-selfies and cowboys among them.
About the Storyteller
Historically, clay figures have been present in the Pueblo pottery tradition for more than a thousand years. However, figures and effigies were denounced as "works of the devil" by the Spanish missionaries in New Mexico between 1540 and 1820. Before and after that time the art of making figurative sculpture flourished, especially at Cochiti Pueblo. At Cochiti, the forms of animals, birds, caricatures of outsiders and, more recently, images of mothers and grandfathers telling stories and singing to children have multiplied.
The "storyteller" is an important role in the tribes as parents are often too busy working and raising kids to pass on their tribal histories. The Native American people did not develop a written language to record anything for posterity. Some tribes still refuse to create one. The closest thing they had to a written language was recorded on pottery and textiles, in the form of painted designs that decorate that pottery and textiles.
The storyteller's role was to preserve and retell and pass down the oral history of his people in their native language. In most tribes that role was fulfilled by elder men.
The first recorded storyteller figure was created in 1964 by Cochiti Pueblo potter Helen Cordero in memory of her grandfather, Santiago Quintana. She gathered her clay from a secret sacred place on the lands of her pueblo. Then she hand-coiled, hand painted and fired that first storyteller figure the traditional way: in the ground. Helen never used any molds or kilns to make her pottery.
Helen's creation immediately struck a chord throughout all the pueblos as the storyteller is a figure central to all their societies. Most tribes also have the figure of the Singing Maiden in their pantheon and in many cases, the mix of Singing Maiden and Storyteller has blurred some lines in the pottery world.
Today, as many as three hundred potters in thirteen pueblos have created storytellers. Their storytellers are not only men and women but also Santa’s, mudheads, koshares, bears, owls, eagles and other animals, sometimes encumbered with children numbering more than one hundred! Each potter has also customized their storyteller figures to more closely reflect the styles and dress of their own tribes, often even of their own clans.
Benigna Medina Madelena Family Tree - Jemez Pueblo
Disclaimer: This "family tree" is a best effort on our part to determine who the potters are in this family and arrange them in a generational order. The general information available is questionable so we have tried to show each of these diagrams to living members of each family to get their input and approval, too. This diagram is subject to change should we get better info.
Benigna Medina was born and raised at Zia Pueblo, learning to make pottery the Zia way as she grew up. Then she married Ramon Madelena from Jemez Pueblo and moved to his home there. She infused the Jemez potters of the time with Zia methods, forms and designs, strengthening a very weak Jemez tradition: the Spanish had virtually destroyed all Jemez traditions 200 years before and recovery was very hard.
- Benigna Medina Madelena (c.1880-) & Ramon Madelena
- Persingula M. Gachupin (ca. 1910-1994) & Joe R. Gachupin
- Marie G. Romero (1927-)
- Laura Gachupin (1954-)
- Benina Foley (1982-)
- Gordon Foley (1975-)
- Maxine Toya (1948-)
- Dominique Toya (1971-)
- Mariam Toya (1974-)
- Laura Gachupin (1954-)
- Leonora G. Fragua (1938-)
- Matthew Fragua (1963-)
- Virginia Ponca Fragua (1961-) & M. Pecos
- Brandon Pecos Fragua (1993-)
- Bertha Gachupin (1954-)
- Antonia Gachupin (1970s-) & Albert Yepa
- Kajzia Gachupin (1991-)
- Kiana Gachupin (1993-)
- Okoya Gachupin
- Antonia Gachupin (1970s-) & Albert Yepa
- Marie G. Romero (1927-)
- Elcira Madelena (c.1915-)
- Mary Rose Toya
- Eloise Toya
- Norma Toya
- Mary Rose Toya
- Josephita Madelena
- Reyes Marie Madelena-Butler (1938-)
- Shannon Madelena-Ellington
- Reyes Marie Madelena-Butler (1938-)