| Dimensions | 2.25 × 2.25 × 1 in |
|---|
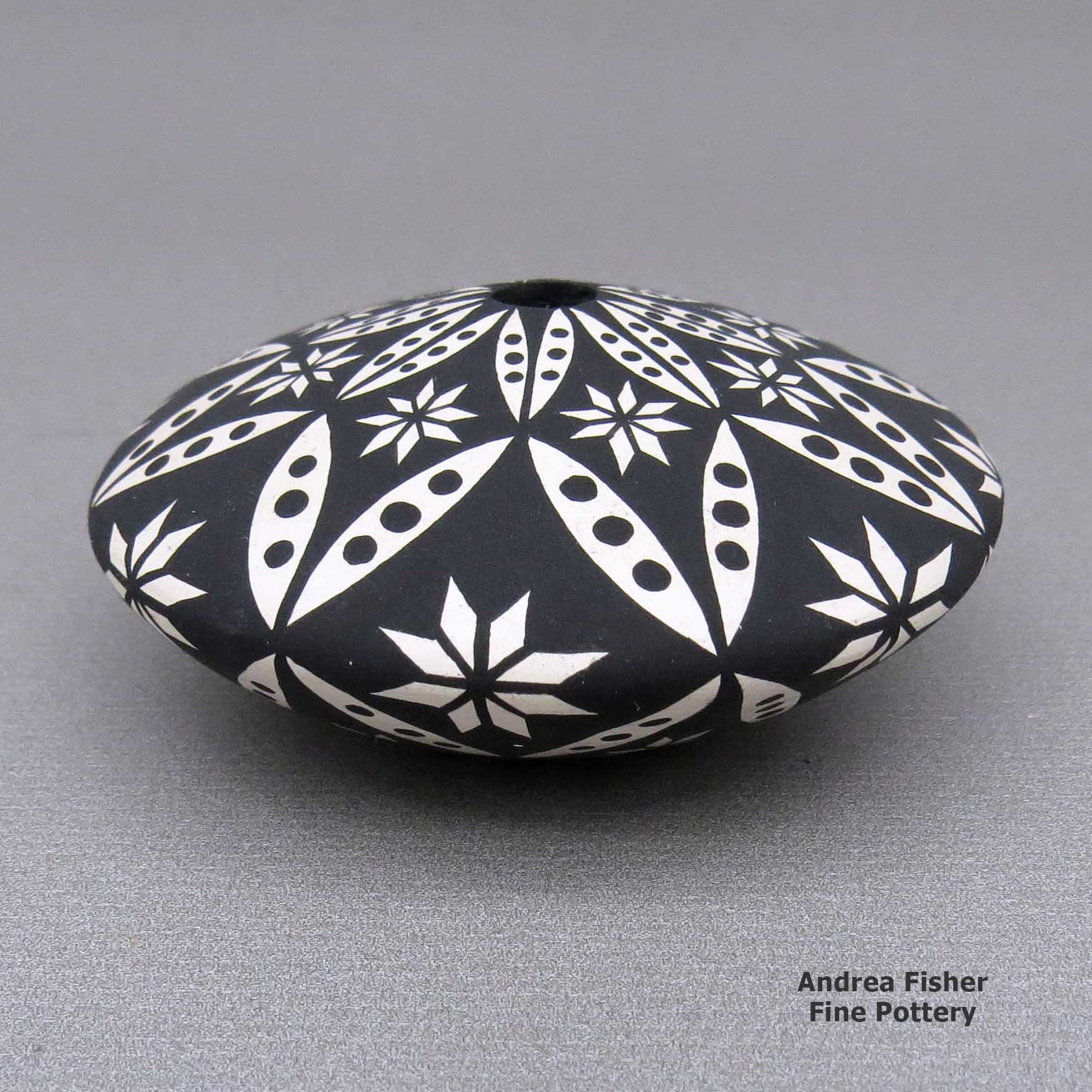
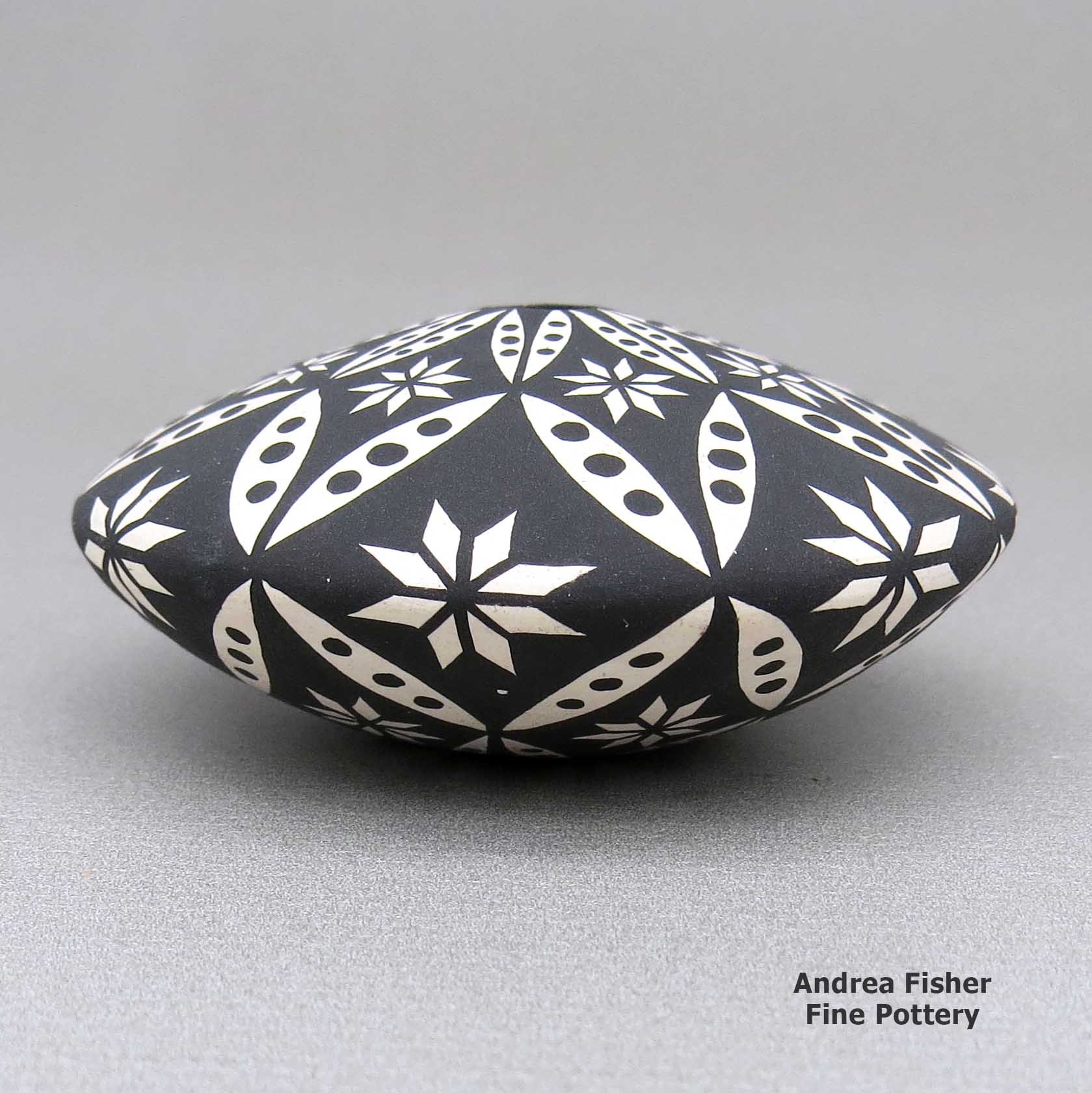
Dorothy Torivio, zzac2m534, Small black and white jar with geometric design
$350.00
A small black-on-white jar decorated with a snowflake pattern and geometric design
In stock
Brand
Torivio, Dorothy
Dorothy made traditional polychrome and black-on-white bowls, jars, seed pots, deer, owls and other figures. Dorothy is most known for her innovative seed pots, usually painted with eye-dazzling geometric designs. They earned her many awards, beginning with a Best of Division, Traditional Pottery at the 1984 Santa Fe Indian Market. During that same Indian Market Dorothy was also awarded a First Place ribbon in the Traditional Jars category and a Second Place ribbon in the Seed Pots category.
Dorothy and her pottery were featured in Susan Peterson's The Legacy of Generations: Pottery by American Indian Women exhibition that began at The National Museum of Women in the Arts in 1997 in Washington, DC, and traveled to several museums around the country through 1997 and 1998.
Dorothy passed her knowledge on to her niece, Sandra Victorino, well before she passed in 2011.
Some Exhibits that featured pieces by Dorothy
- Home: Native People in the Southwest. Heard Museum. Phoenix, Arizona. Opened May 22, 2005
- New Directions in Southwestern Native American Pottery. Peabody Essex Museum. Salem, Massachusetts. November 16, 2001 - March 17, 2002
- The Legacy of Generations: Pottery by American Indian Women. The National Museum of Women in Arts. Washington, DC. October 9, 1997 - January 11, 1998
- The Legacy of Generations: Pottery by American Indian Women. Heard Museum. Phoenix, Arizona. February 14, 1998 - May 17, 1998
- Master Artists of the Southwest. Quintana Galleries. Portland, Oregon. September 24-26, 1993
- Fifth Annual Hollywood Premiere. Four Seasons Hotel. Los Angeles, California. November 23, 1991
- The Perfection of Southwest Pottery. Gallery 10. Scottsdale, Arizona. February 21, 1991
- Our 1990 Indian Market Week Shows. Gallery 10. Santa Fe, New Mexico. August 10-17, 1990
- New Works by Jody Folwell, Dorothy Torivio and Jacquie Stevens. Gallery 10. Scottsdale, Arizona. March 8, 1990
- The Absolute Best of Indian Market. Gallery 10. Four Seasons Hotel. Los Angeles, California. November 18-20, 1989
- Exhibition of Richard Zane Smith, Dorothy Torivio, LuAnn Tafoya and Thomas Natseway. Gallery 10. Scottsdale, Arizona. March 2-8, 1989
- Individual Statements of Style. Gallery 10. Scottsdale, Arizona. February 25, 1988
- The Best of Indian Market '87: Six Nationally Prominent Native American Artists. Four Seasons Hotel. Los Angeles, California. November 28-29, 1987
- Exhibition of Richard Zane Smith, Dorothy Torivio, Polly Folwell and Fred Myers. Gallery 10. Scottsdale, Arizona. February 5-17, 1987
- Innovators in Southwestern Native American Ceramics. Gallery 10. Scottsdale, Arizona. February 6-19, 1986
- Jewels of the Southwest. Gallery 10. Scottsdale, Arizona. December 3, 1985 - January 4, 1986
- The Pottery of Jody Folwell and Grace Medicine Flower, with "Rising Stars" including Dorothy Torivio & Richard Zane Smith, potters. Morning Star Gallery. Santa Fe, New Mexico. August 12-17, 1985
Some Awards earned by Dorothy
- 2004 Heard Museum Guild Indian Fair & Market, Classification VIII - Pottery, Division A - Traditional/Native clay/hand (painted): Best of Division
- 1998 Santa Fe Indian Market, Classification II - Pottery, Division F - Traditional pottery, painted designs on matte or semi-matte surface, all forms except jars, Category 1302 - Seed bowls (over 7" in diameter): First Place
- 1995 Santa Fe Indian Market, Classification II - Pottery, Division G - Traditional pottery, painted designs on matte or semi-matte surface, all forms except jars, Category 1402 - Seed bowls (over 7" in diameter): Second Place
- 1994 Santa Fe Indian Market, Classification II - Pottery, Division G - Traditional pottery, painted designs on matte or semi-matte surface, all forms except jars, Category 1402 - Seed bowls (over 7" in diameter): First Place
- 1994 Santa Fe Indian Market, Classification II - Pottery, Division G - Traditional pottery, painted designs on matte or semi-matte surface, all forms except jars, Category 1406 -Other vases: Second Place
- 1984 Santa Fe Indian Market, Classification II - Pottery, Division F - Traditional pottery, painted designs on matte or semi-matte surface: Best of Division. Awarded for jar
- 1984 Santa Fe Indian Market, Classification II - Pottery, Division F - Traditional pottery, painted designs on matte or semi-matte surface, Category 1202 - Jars, Acoma or Laguna: First Place
- 1984 Santa Fe Indian Market, Classification II - Pottery, Division F - Traditional pottery, painted designs on matte or semi-matte surface, Category 1205 - Seed bowls: Second Place
- 1984 Heard Museum Guild Native American Invitational Arts Show: Best of Pottery Award. Awarded for artwork: Large Brown Jar
- 1984 Heard Museum Guild Native American Invitational Arts Show: Judge's Choice Award - Dennis Lyons. Awarded for artwork: Small Seed Jar
- 1984 Heard Museum Guild Native American Invitational Arts Show: Judge's Choice Award - Clara Lee Tanner. Awarded for artwork: Small Seed Jar
- 1984 Heard Museum Guild Native American Invitational Arts Show, Classification II - Pottery, Division A - Traditional Construction and Firing Method: First Place. Awarded for artwork: Large Brown Jar
- 1984 Heard Museum Guild Native American Invitational Arts Show, Classification II - Pottery, Division D - Miniatures (Under 2 1/4"): First Place. Awarded for artwork: Miniature Seed Jar
- 1987 Gallup InterTribal Indian Ceremonial, Category VI - Pottery, Jar, Seed Jar: Second Place
- 1987 Gallup InterTribal Indian Ceremonial, Category VI - Pottery, Decorated, any object: First Place
A Short History of Acoma Pueblo
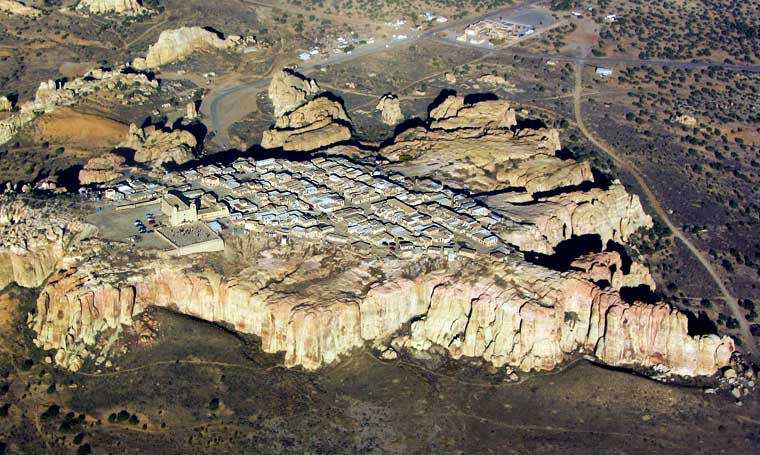

According to Acoma oral history, the sacred twins led their ancestors to "Ako." Ako turned out to be a magical mesa composed mostly of white rock. There the sacred twins instructed the ancestors to make that mesa their home. Acoma Pueblo is called "Sky City" because of its position atop the high mesa.
Acoma, Old Oraibi (at Hopi) and Taos all lay claim to being the oldest continuously inhabited community in the U.S. Those competing claims are hard to settle as each village can point to archaeological remnants close by to substantiate each village's claim. Acoma is located about 60 miles west of Albuquerque in a landscape littered with the ruins of ancient pueblos, many more than 1,000 years old.
The people of Acoma have an oral tradition that says they've been living in the same area for more than 2,000 years. Archaeologists feel more that the present pueblo was established near the end of the major migrations in the 1200 and 1300s. The location is essentially on the boundary between the Mogollon (Mimbres), Hohokam (Salado) and Anasazi (Ancestral Puebloan) cultures. Each of those cultures has had an impact on the styles and designs of Acoma pottery, especially since modern potters have been getting the inspiration for many of their designs from pot shards they have found while walking on pueblo lands.
Francisco Vasquez de Coronado ascended the cliff to visit Acoma in 1540. He afterward wrote that he "repented having gone up to the place." But the Spanish came back later and kept coming back.
Around 1598 relations between the Spanish and the Acomas took a nasty turn with the arrival of Don Juan de Oñaté and the soldiers, settlers and Franciscan monks that accompanied him. After making the arduous ascent to the mesa top, de Oñaté decided to force the Acomas to swear loyalty to the King of Spain and to the Pope. When the Acomas realized what the Spanish meant by that, a group of Acoma warriors attacked a group of Spanish soldiers and killed 11 of them, including one of de Oñaté's nephews.
De Oñaté retaliated by attacking the pueblo. His troops burned most of it and killed more than 600 people. Another 500 people were imprisoned by the Spanish. Males between the ages of 12 and 25 were sold into slavery. 24 men over the age of 25 had their right foot amputated. Many of the women over the age of 12 were also forced into slavery. Most were parceled out among Catholic convents in Mexico City.
Two Hopi men were also captured at Acoma. The Spanish cut one hand off of each and sent them home to spread the word about Spain's resolve to subjugate the inhabitants of Nuevo Mexico. Spanish monks did make the trip a few years later but Spanish military made hardly an appearance in Hopiland.
When word of the massacre (and the punishments meted out after) got back to King Philip in Spain, he banished Don Juan de Oñaté from Nuevo Mexico. Some Acomas had escaped that fateful Spanish attack and returned to the mesa top in 1599 to begin rebuilding.
In 1620 a Royal Decree was issued which established civil offices in each pueblo and Acoma got its first governor. That didn't help the people any as those appointed to the government positions were also those most on the take with the Spanish authorities. By 1680, the situation between all of the pueblos and the Spanish had deteriorated to the point where the Acomas were extremely willing participants in the 1680 Pueblo Revolt.
After the successful Pueblo Revolt pushed the Spanish back to Mexico, refugees from other pueblos began to arrive at Acoma. Most feared the eventual Spanish return and probable reprisals. That strained the resources of Acoma badly. Then the Spanish returned in force and residents of the pueblo had to make a hard decision. Many of the refugees chose to try a peaceful solution: they relocated north to the ancient Laguna area and made peace with the Spanish as soon as they reappeared in the region. Acoma held out against the Spanish for awhile but soon capitulated.
Over the next 200 years, Acoma suffered from breakouts of smallpox and other European diseases to which they had no immunity. At times they would side with the Spanish against nomadic raiders from the Ute, Apache and Comanche tribes. Eventually New Mexico changed hands. Then the railroads arrived and Acoma became dependent on goods made in the outside world.
For many years the villagers were content on the mesa. Now most live in villages on the valley floor where water, electricity and other necessities are easily available. A few families still make their permanent home on the mesa top. The old pueblo is used almost exclusively these days for ceremonial celebrations.

For more info:
Acoma Pueblo at Wikipedia
Pueblo of Acoma official website
Pueblos of the Rio Grande, Daniel Gibson, ISBN-13:978-1-887896-26-9, Rio Nuevo Publishers, © 2001
Acoma & Laguna Pottery, Rick Dillingham with Melinda Elliott, ISBN 0-933452-32-2, School of American Research Press, © 1992
Upper photo courtesy of Marshall Henrie, Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported License
About Western Keresan Designs
Those of the Western Keres tradition have a plethora of traditional designs. A reason for that is they have occupied a region on the boundary between the Mogollon cultures to the south and the Ancestral Puebloan cultures to the north. And some of them have been living and working in the same place for a thousand years or more. They have also been making and breaking pottery the whole time. The area of Laguna has been more or less populated for a similar amount of time and, when populated, the Lagunas have moved around more than the Acomas.
Because Acoma and Laguna are located in that boundary area between Chaco Canyon influence to the north and Mogollon-Mimbres Valley influence to the south, designs and techniques have been coming and going across the landscape for many years. Over time, broken potsherds covered with multiple designs have fallen to the ground almost everywhere, just waiting to be picked up by someone, have their designs copied and revived, and their most basic constituents ground and mixed with fresh clay and to be reborn as pots again.
In the 1950s, that started happening a lot, potsherds being picked up and their designs revived, that is. Many of those designs have since been traced back to artisans in the Mimbres Valley working before 1150 CE. They had a unique perspective on the birds, animals, insects and people of their world, and used that perspective to draw and paint unique patterns. Many of those patterns are still being recreated on pottery across the Pueblo world, but especially at Acoma and Laguna. Central to the design palette are stories from the adventures of the Twin Warriors. While some Flower World iconography is also present in the Acoma design palette, there is extremely little from the kachina cults of the Hopi and Zuni.
One of the more recent "traditional" Acoma designs is the parrot holding a twig with berries in its claws. Often there is a rainbow above or below the parrot. Parrots are not natural in New Mexico, they had to have been imported. Before about 1450 CE, there was a trade in parrots and macaws through Paquimé to regions in the north. The remains of macaws have been pretty common but the remains of green parrots have only been recovered from three pueblos: Cicuyé, Paquimé and Grasshopper Pueblo in Arizona. The ancient-most Acoma parrot design has a Mimbres/Mogollon heritage while the parrot most painted today looks more like it came from an Amish trader's box. And it likely did.
With the arrival of Spanish colonists in New Mexico, pueblo potters changed their pottery to meet the demands of a new market. Their shapes and designs changed with that. Everything changed again with the arrival of Amish traders with their enameled cookware in the 1850s. The "new" Acoma parrot was pictured on the boxes those pots came in. The parrot came into being around 1880 and has been in use so long now it is considered "traditional."
Pottery was always in production at Acoma but from about 1600 to about 1950, it was heavily influenced by colonial shapes and designs. Eventually, the potters were reduced to producing items for the tourist trade to make ends meet, and that didn't go over so well either. Their own interest in making pottery fell off. Lucy Lewis, Jessie Garcia and Marie Z. Chino started decorating their pieces with their new interpretations of ancient Mimbres, Tularosa and Cibola designs in the 1920s and interest, both outside and inside the pueblo, grew again from there.
Laguna was impacted more heavily by the newcomers. Two Methodist missionaries married women in the pueblo and one of them shortly had himself elected President of the Pueblo. One of the first things he did was order the destruction of all the kivas on Laguna Pueblo land. That caused a schism and many Lagunas relocated to Isleta for a number of years (some of them are still there).
The Southern branch of the Transcontinental Railroad ran across Laguna Pueblo, and offered jobs to many of the men. That essentially ended the making of pottery by most tribal members. Then uranium was discovered under pueblo lands and more men went to work mining for that. Only a couple families passed the traditional knowledge down, until it eventually reached Evelyn Cheromiah. Nancy Winslow, an Anglo woman from Albuquerque, helped Evelyn obtain a grant to teach pottery making on the pueblo and a small revival started from there. Laguna potters, too, work their designs from designs they find on potsherds they find lying on the ground around the old pueblos. Their designs are very much like those of Acoma, usually just with more white space and bolder lines.
About Jars
The jar is a basic utilitarian shape, a container generally for cooking food, storing grain or for carrying and storing water. The jar's outer surface is a canvas where potters have been expressing their religious visions and stories for centuries.
In Sinagua pueblos (in northern Arizona), the people made very large jars and buried them up to their openings in the floors of the hidden-most rooms in their pueblo. They kept those jars filled with water but also kept smaller jars of meat and other perishables inside those jars in the water. It's a form of refrigeration still in use among indigenous people around the world.
Where bowls tend to be low, wide and with large openings, jars tend to be more globular: taller, less wide and with smaller openings.
For a potter looking at decorating her piece, bowls are often decorated inside and out while most jars are decorated only on the outside. Jars have a natural continuity to their design surface where bowls have a natural break at the rim, effectively yielding two design surfaces on which separate or complimentary stories can be told.
Before the mid-1800s, storage jars tended to be quite large. Cooking jars and water jars varied in size depending on how many people they were designed to serve. Then came American traders with enameled metal cookware, ceramic dishes and metal eating utensils...Some pueblos embraced those traders immediately while others took several generations to let them and their innovations in. Either way, opening those doors led to the virtual collapse of utilitarian pottery-making in most pueblos by the early 1900s.
In the 1920s there was a marked shift away from the machinations of individual traders and more toward marketing Native American pottery as an artform. Maria Martinez was becoming known through her exhibitions at various major industrial fairs around the country and Nampeyo of Hano was demonstrating her art for the Fred Harvey Company at the Grand Canyon. The first few years of the Santa Fe Indian Market helped to solidify that movement and propel it forward. It took another couple generations of artists to open other venues for their art across the country and turn Native American art into the phenomenon it has become.
Today's jars are artwork, not at all for utilitarian purposes, and their shapes, sizes and decorations have evolved to reflect that shift.
Teofila Torivio Family Tree - Acoma Pueblo
Disclaimer: This "family tree" is a best effort on our part to determine who the potters are in this family and arrange them in a generational order. The general information available is questionable so we have tried to show each of these diagrams to living members of each family to get their input and approval, too. This diagram is subject to change should we get better info.
- Teofila Torivio & Antonio Torivio
- Katherine Analla
- Lolita Concho (1914-2000)
- Dorothy Torivio (daughter-in-law) (1946-2011)
- Sandra Victorino (niece) (1958-) & Cletus Victorino Sr.
- Cletus Victorino Jr. (1978-)
- Sandra Victorino (niece) (1958-) & Cletus Victorino Sr.
- Dorothy Torivio (daughter-in-law) (1946-2011)
- Concepcion "Connie" Torivio Garcia (c. 1925-)
- Juanita Torivio Keene & Gus Keene Sr.
- Adrienne Roy Keene
- Gus Keene Jr.
- Waya Gary Keene
- Mamie Torivio Ortiz
- Frances Pino Torivio (1905-)
- Wanda Aragon (1948-) & Marvis Aragon Sr.
- Clarice Aragon (1972-)
- Marvis Aragon Jr. & Delores Aragon (daughter-in-law) (1969-)
- Ruth Paisano
- Lilly Maria Salvador (1944-) & Wayne Salvador
- Carleen Salvador
- Darlene Salvador
- Roberta Salvador
- Ryan Paul Salvador
- Wanda Aragon (1948-) & Marvis Aragon Sr.