| Dimensions | 1.25 × 1.25 × 2.5 in |
|---|---|
| Condition of Piece | Excellent |
| Date Born | 2023 |
| Signature | Isleta W/T KD, with hallmarks |
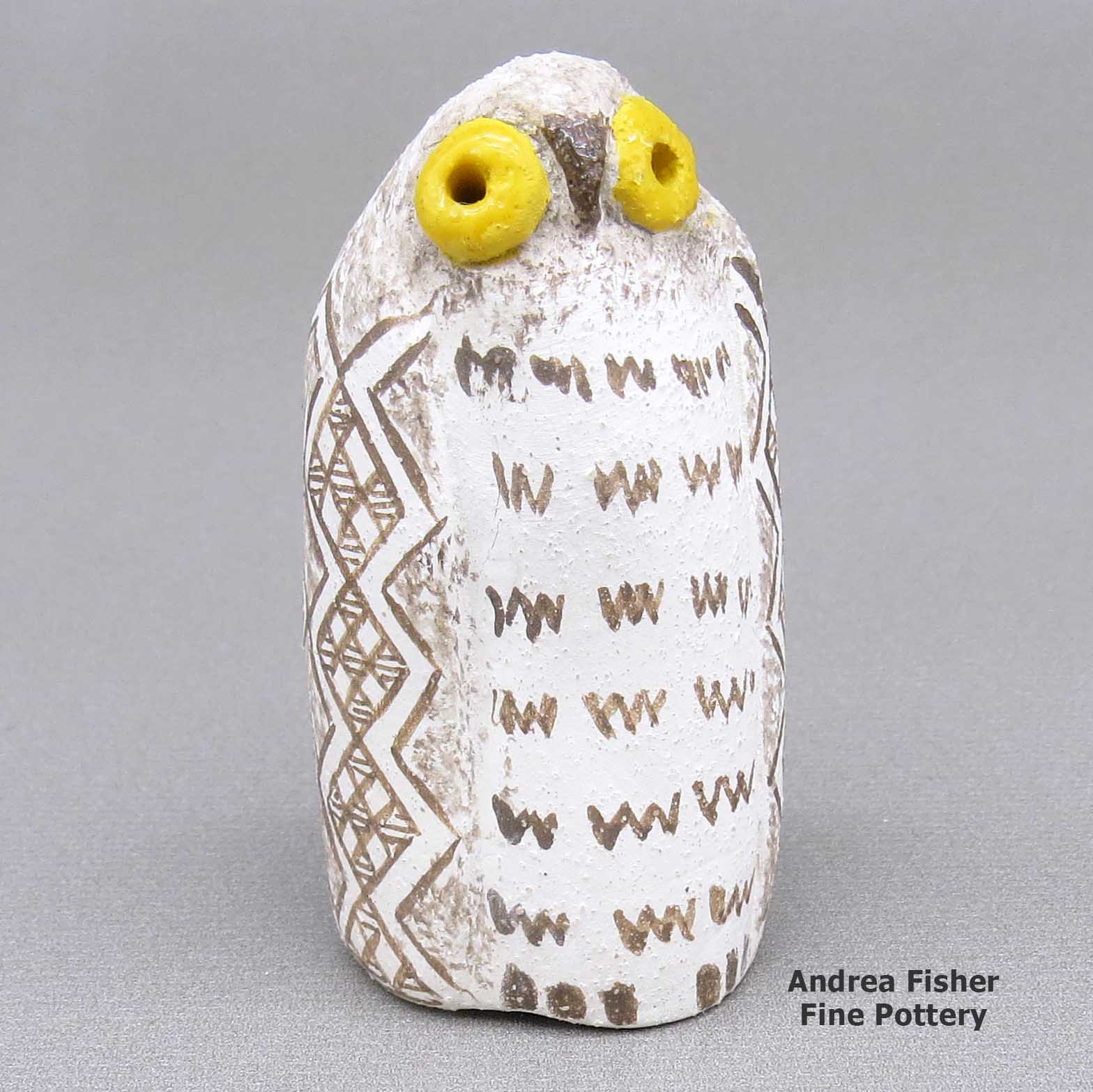
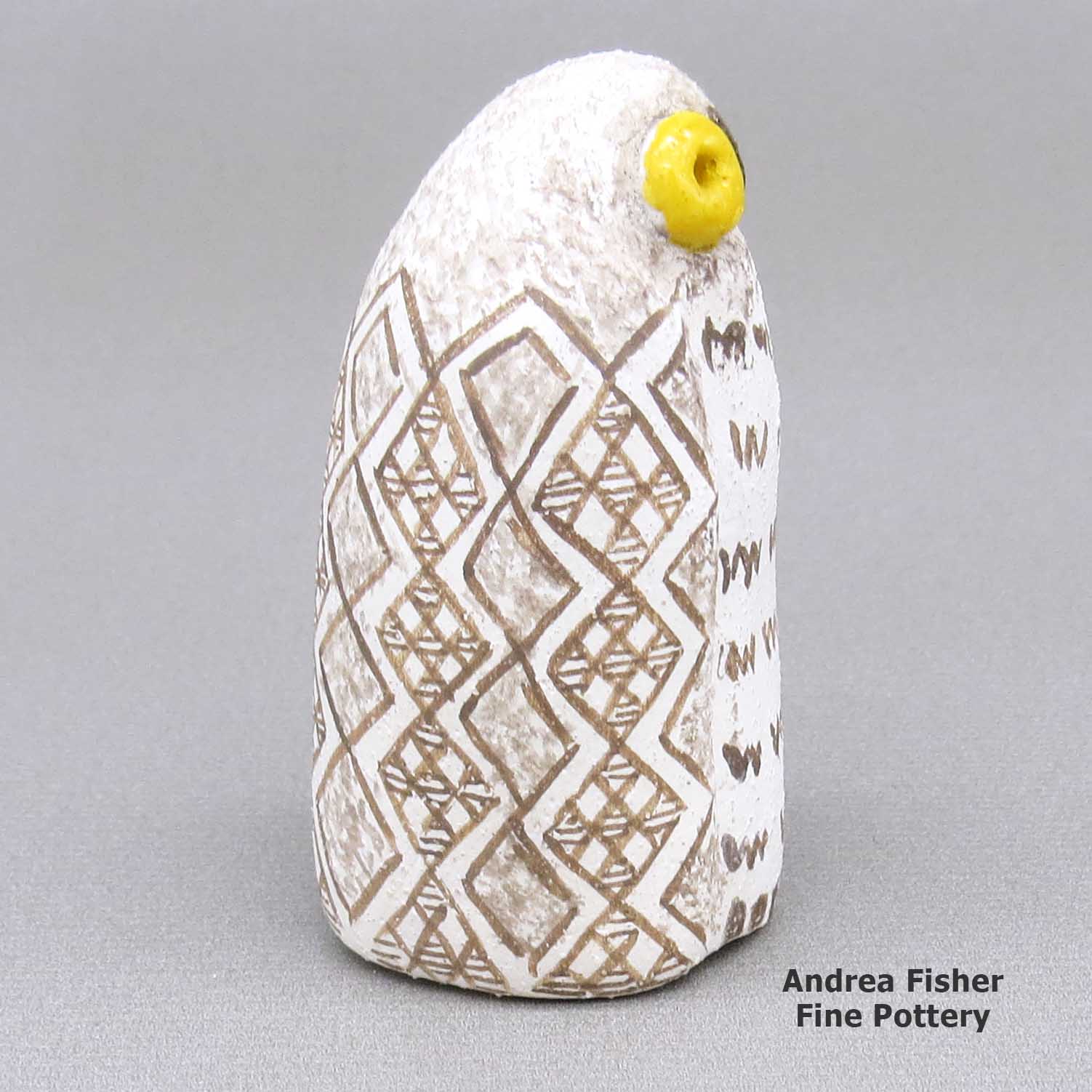
Kimo DeCora, zzle3b282m5, Owl figure with a geometric design
$165.00
A small polychrome owl figure decorated with a fine line and geometric design
In stock
Brand
DeCora, Kimo
After finishing high school, Kimo attended Haskell Indian Nations University and studied off-set lithography. He became a certified off-set pressman, then ten years later he got interested in painting. At first he drew his inspiration from his love of the outdoors. Then he started to connect with ancient Anasazi and Mimbres ruins and some of the artifacts he found there.
He learned the basics of traditional pottery making on his own but he also learned through watching Cipriano Romero Medina and John Montoya at work.
Kimo's favorite shapes to make are bowls, jars, small owls and his trademark miniatures. Over the years his pieces have earned him many blue ribbons at the Winnebago, NE, Fine Arts Show (18 ribbons in 1983 alone!), more blue ribbons at the Albuquerque CeramicFest and even more blue ribbons at Andrea Fisher Fine Pottery's annual Best of the Best Shows.
Kimo told us his inspiration comes from his pre-Columbian ancestors, specifically the people from the Mimbres Valley in southern New Mexico. It's their designs he most often uses to decorate his work. His signature reflects his tribal affiliation (W/T: Winnebago Ho-Chunk / Isleta-Tiwa), along with some subconscious doodling for a hallmark.
The Winnebago/Ho-Chunk were never prolific creators of pottery but they have been known to paint and do fancy beadwork. Kimo doesn't do beadwork but he does craft and paint Christmas ornaments and miniature pots and figures. He also creates paintings in traditional Pueblo and nouveau-Western Pueblo styles. Kimo told us he practices Tai Chi before he does any painting as it enhances his brushwork and helps him to be more creative and productive.
In Kimo's words: "I'm not the extrovert type and, like many others, don't need to be noticed to be happy ('Call me Hieronymous, cuz I like being anonymous'). It's a blessing to enjoy good health and be appreciated for the medium I express myself with. I also believe humor is a good thing."
A Short History of Isleta Pueblo
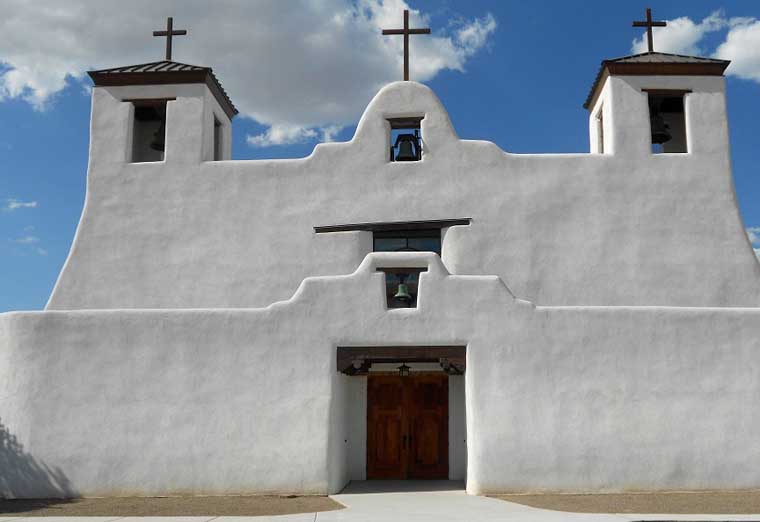

Isleta Pueblo was founded in the 1300s. Archaeologists have put forth various ideas as to where the people came from with some scholars saying they migrated north from Mogollon/Mimbres settlements to the south while others say they migrated southeastward from either Chaco Canyon in the 1100s and 1200s or from the Four Corners area in the 1200s and 1300s. There is every possibility they are an indigenous Tano population that was merged with Aztec migrants coming north from central Mexico and they were never part of the Chacoan world. Their Tiwa language is shared with nearby Sandia Pueblo and a very similar tongue is spoken to the north at Taos and Picuris Pueblos. The two dialects are sometimes referred to as Southern and Northern Tiwa. The Taos people also consider that some of their ancestors migrated north from Aztec lands long ago while others came from the north.
When the Spanish arrived in the area they named the pueblo "Isleta" (meaning: island). The residents were relatively accommodating to the Spanish priests when compared to the reception the same priests got in other areas of Nuevo Mexico (making Isleta something of an "island of safety" for the Spanish in an ocean of hostility). When the Pueblo Revolt of 1680 happened, Isleta either couldn't or wouldn't participate in the rebellion.
When the Spanish governor was evicted from Santa Fe he went to Albuquerque, then to Isleta and gathered his troops. With warriors from the northern pueblos harassing their every move, none of the Spaniards wanted to go back and fight so when they left Isleta and headed south, many Isletans went south to the El Paso area with them. Those who went south were allowed to establish their own pueblo at Ysleta del Sur, a place that at the time was beyond the boundaries of the village of El Paso.
Other Isletans fled to the Hopi settlements in Arizona and returned after the fighting was clearly over, many with Hopi spouses. When the Spanish returned in 1682 they found the Isleta mission church burned and the main structure was being used as a livestock pen. When Don Diego de Vargas came in 1692 with troops intent on reconquering New Mexico, they found the whole village of Isleta empty and burned.
The governor ordered the pueblo be rebuilt and resettled so residents were brought in from Taos and Picuris to the north and from Ysleta del Sur to the south. By 1720 a new, more grandiose mission had been built on the foundations of the first.
Over the next century some dissident members of the Laguna and Acoma Pueblo communities migrated to Isleta. While they were welcomed into the main Isleta pueblo at first, friction developed over the years until in the late 1800s, the small communities of Oraibi and Chicale were established. Most of the newcomers moved to one or the other but some returned to Acoma and Laguna.
For more info:
Pueblo of Isleta at Wikipedia
Pueblo of Isleta official website
About Figures and Figurines
Generally, "Figure" denotes a real or mythic creature, like an owl or human or katsina or Corn Maiden. Whether form or decoration, all Puebloan pottery figures are meant to invoke particular spiritual essences. That's why "effigy" is used almost as often as "figure" to denote these pieces.
Among most Puebloans, the figure of an owl, for example, signifies all the physical and spiritual aspects attributed to the owl. It's a form of prayer to the spirit of "Owl" and the appropriately decorated physical form is meant to make that spirit manifest. However, to the Zuni people an owl is a good omen and to the Tewa people, an owl is a bad omen. Some potters at Santa Clara have made owls anyway, they just shaped and decorated them to reflect that "badness."
That explanation may make more sense in the case of the Corn Maiden as she is a mythic entity whose existence revolves around the most ubiquitous food staple in the Puebloan world: corn (maize). All representations of the Corn Maiden are meant to invoke her benevolence and abundance for their people. Because of her mythical/spiritual nature, different pueblos have slightly different physical forms for her but they all incorporate the basic form of a female human face on an ear of corn.
The potters of Tesuque turned out thousands of muna figures (also known as rain gods)for several decades, until they virutally burned out their pottery tradition. These muna had very specific shapes but were decorated with everything from micaceous slips to incised lines to polychrome geometric designs to poster paints. They were also made purely for domestic American consumption, sometimes delivered by the barrel to be used as prizes and giveaways.
The Storyteller is another figure based on Puebloan tradition: a tribal elder singing the stories of the tribe's oral history to the children. The original was based on the traditional cultural story: a grandfather singing his part of the story in his native language so the children learn both the language and their identity against the backdrop of that history. Shortly, the storyteller form was duplicated in several other pueblos, each pueblo's potters adapting the form to their local situation. In some places, the grandmother became the primary sex of their storytellers. At Jemez, that responsibility was shared between grandmothers and grandfathers. Then some potters in search of new niches in the marketplace branched into making "spirit figure" storytellers, like eagles, ravens, hummingbirds, cats and dogs. Some Zuni potters have made storyteller owls.
Similar to the Storyteller is the Story Time: a set of separate children displayed around a larger central singing figure.
The Nativity set (also known as nacimiento) is a set of figures based on the intersection of Puebloan mythologies and stories they heard from Christian missionaries. Those potters who make them also tend to favor dress, shapes and designs that reflect their own heritage(s). The first few nativities made at Tesuque Pueblo were decorated with Spanish colonial costumes but that soon changed and every nativity made since has a distinct blend of Native American and Christian, with no other reference to colonialism. The "Singing Angel" (a single standing figure with outstretched wings and hands clasped together in prayer) and "Flight to Egypt" (usually depicting Mary with a baby Jesus on the back of a donkey and a standing Joseph nearby holding the rein) are similar mixes of tribal and Christian figures. The miniature nativities made by Santa Clara/Dineh artist Linda Askan clearly show Dineh religious influence in the headresses worn by Joseph, the angel and the three wise men. At the same time, the Dineh Folk Art nativities made by Jonathan Chee are based on the realities of daily Dineh life: the three wise men wear wide-brim hats and blue jeans, and bring gifts of salt and 50-pound bags of flour.
Pueblo and Dineh artists also make a full zoo of domesticated, farm and wild animal figures: horses, donkeys, cows, chickens, pigs, sheep, turkeys, giraffes, elephants, dogs, cats, mermaids, women-dressed-up-and-taking-selfies and cowboys among them.
About Bird Elements
One of the main tenets of the Flower World ideology is that birds are messengers to and from Paradise. They carry our prayers to Heaven and they bring back the responses. Not all the pueblos accepted the Flower World ideology but it seems almost everyone, almost everywhere, agrees that birds are the messengers of Heaven. All pueblos do have multiple designs that incorporate feathers, if feathers aren't the main element of the design.
The Flower World ideology originated in central Mexico and most likely traveled north to the pueblos in the company of missionaries and long-distance traders. Turquoise was taken south while tropical birds, copper bells, seashells, and textiles (with particular spiritual designs on them), along with other spiritual items, were taken north. Going either way, almost everyone passed by Paquimé. The trade routes from the south came together there and the trade routes to the north diverged from there. That business didn't really come together until the first structures went up in the immediate vicinity of Paquimé, around 1150 CE. Then it ended around 1450 CE when the city was abandoned. That was also the end of pilgrims making their way south and then coming north again a few years later. For more than 300 years that traffic had been a major profit center and prestige generator for the people of Paquimé and Casas Grandes. After Paquimé was abandoned, though, the trade and pilrimage routes became far more dangerous. With the advent of the Aztec Empire in central Mexico, being a foreigner in that area became far more dangerous, too. Essentially, the puebloans who had embraced the Flower World ideology were cut off from their Holy Land.
The Flower World Complex, with its symbology, flowed across the American Southwest and eventually reached the Four Corners area. But it arrived at about the same time the kachina cults were coming together and the people were abandoning the Four Corners. The Flower World ideology was felt to be greater than what had come before so it's symbology was basically imprinted on top of that. Then the designs of the kachina cults and other clans were added on top of the Flower World symbology. Then came the Europeans with their designs and spiritual practices.
One of the principals of Native American design is that it is necessary only to note one part of most animals to imply the presence of the whole, especially when it comes to birds and bird elements. A lot of the design on Hopi pottery can only be described as "bird elements," although it is often possible to discern parrot feathers from eagle feathers, and eagletails from other bird's tails.
The Zunis have an ancient "almost-spiral" design that comes from the beaks of their equally ancient "rainbirds." The Zunis also like to make owl figures as owls are a symbol of wisdom to them. To some Northern Tewas, owls are creatures to be feared.
At Acoma they have a "cloudeater," a crane pictured with neck bent over and filling with fish shown sideways in its throat as it swallows them whole. Acoma potters also have a parrot that resembles the parrot found on the sides of the boxes carried by Amish traders back in the day. The parrot is not complete without a branch with leaves, and maybe berries, in its claws.
At Santo Domingo, religious dictates limit what can be imaged on pottery offered to the public. Birds, fish, turtles and flowers are allowed, along with a vast catalog of geometric designs. Images of humans are not. Next door at Cochiti, almost anything goes
The artists of the Mata Ortiz area are resurrecting some of the designs left behind by artists of old but they have no inner connection with the Flower World. Others in today's Mata Ortiz have gone totally contemporary: carving, scratching and painting beautiful images of birds with branches, vines and flowers.






