| Dimensions | 6.5 × 6.5 × 5.25 in |
|---|---|
| Condition of Piece | Excellent |
| Date Born | 2022 |
| Signature | Robert Vigil Nambe |
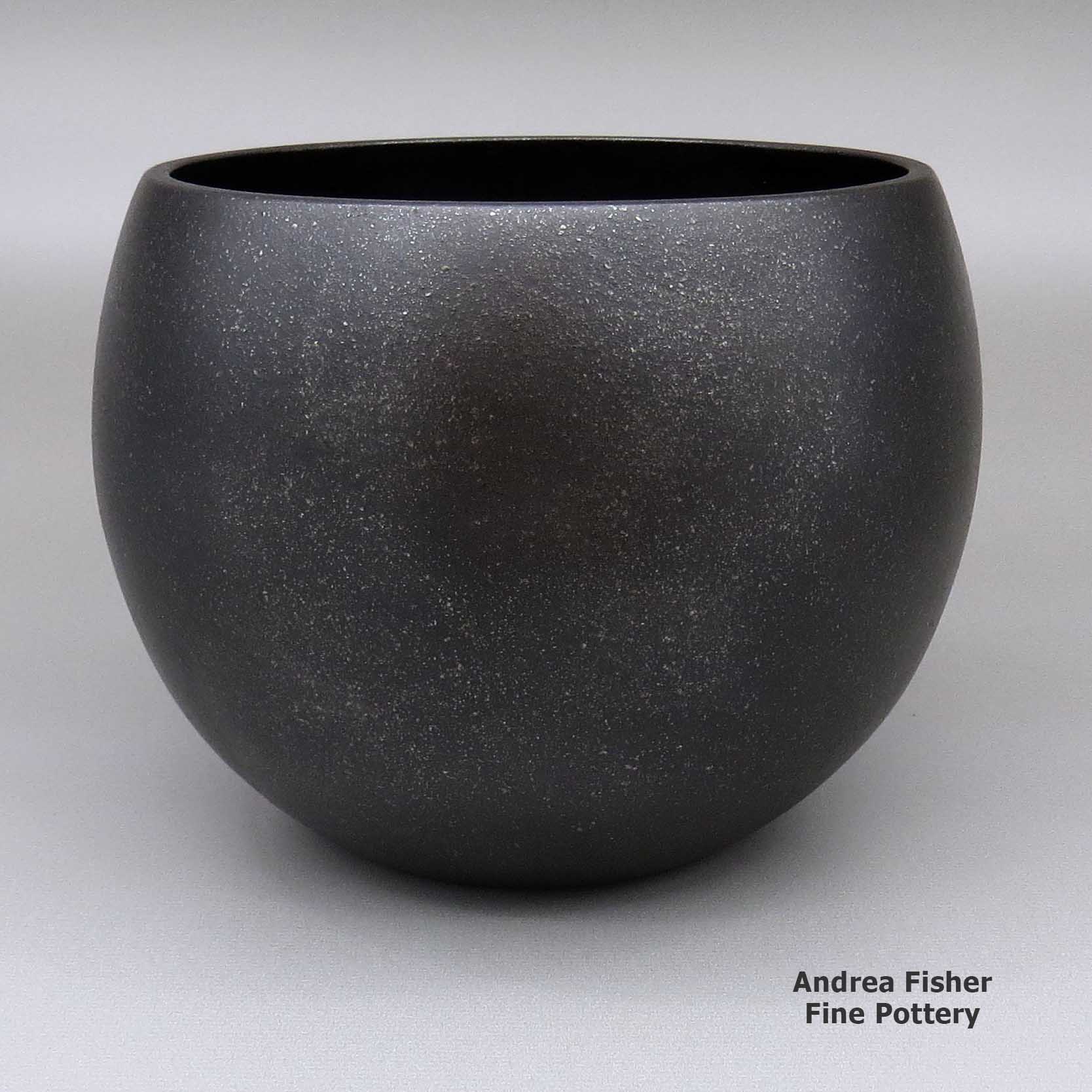
Robert Vigil, zzna2m290, Micaceous black bowl
$375.00
A simple undecorated micaceous black bowl with fire clouds
In stock
Brand
Vigil, Robert
 "I just sit down and start and the clay forms itself through my hands."
"I just sit down and start and the clay forms itself through my hands."Half Nambe Pueblo and half Non-Pueblo, Robert Vigil was born to parents Joe and Alice Vigil in 1965. He first learned the method of making pots with clay coils while in high school in Texas. Then he returned to the pueblo and began to learn from folks like Virginia Gutierrez, his cousin Lonnie Vigil and then from Juan Tafoya of San Ildefonso Pueblo. Robert has been active as a Nambe potter since 1990 working with micaceous jars, bowls, vases, figures and polished redware.
Robert doesn't create giant storage jars like his cousin Lonnie. He much prefers to work on a smaller, more intimate scale. He colors his micaceous pots with fire clouds and other variations produced by the method of firing. There is an elegant purity to his simplistic and understated forms, a deep reflection of his soft spoken manner and gentle spirit.
Robert has told us he prefers the simple shapes and forms and even his carving is gentle. He gets his inspiration from the clay: "I just sit down and start and the clay forms itself through my hands." He's lately been teaching others at his pueblo how to make pottery the traditional way as he doesn't want to see that tradition get lost over time.
Robert has participated in shows at the Wheelwright Museum of the American Indian, at the Eight Northern Pueblos Arts and Crafts Show and at the First Micaceous Pottery Market and Symposium in 1995 in Santa Fe. Pieces of Robert's micaceous pottery are on display at the Minneapolis Art Institute in Minneapolis, MN, and at the Crocker Art Museum in Sacramento, CA, among others.
About Nambé Pueblo
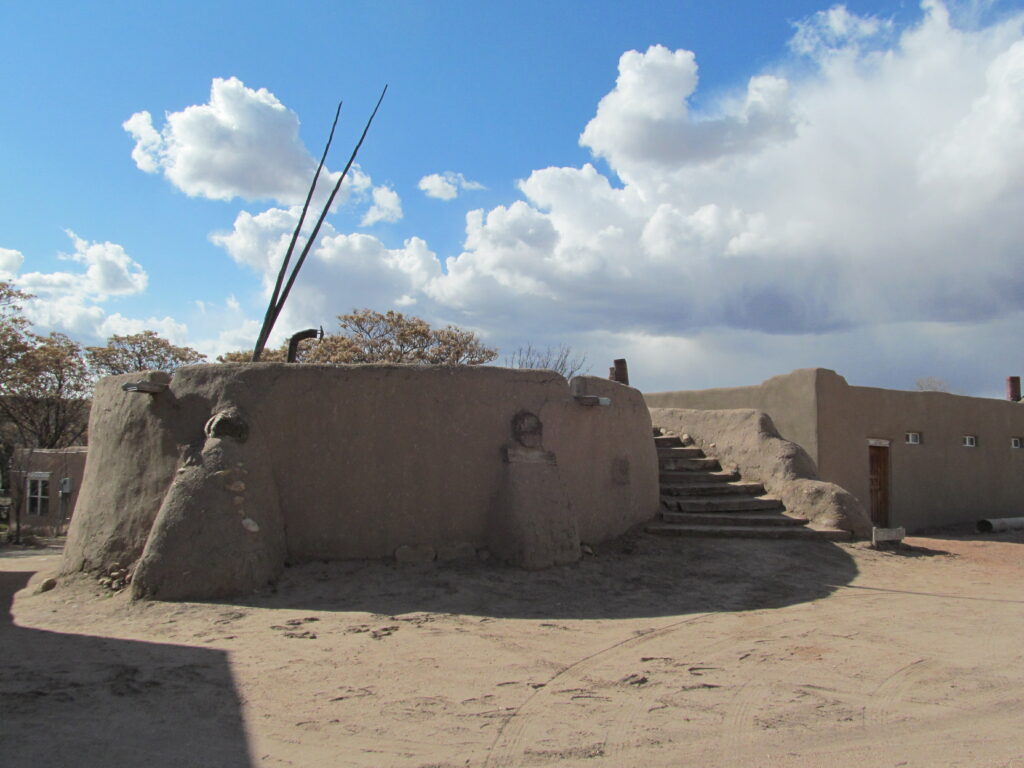

Nambé Pueblo was settled in the early 1300s when a group of Ancestral Puebloans (Anasazi) made their way from what is now the Bandelier National Monument area closer to the Rio Grande in search of more reliable water sources and more arable land.
At first they settled mostly high in the mountains, coming down to the river valleys in the summer to grow crops. Eventually, they felt safe enough to stay in the valleys and slowly abandoned the high mountain villages.
When the Spanish first arrived, Nambé was a primary economic, cultural and religious center for the area. That attracted a large Spanish presence and the nature of that presence caused the Nambé people to join wholeheartedly in the Pueblo Revolt of 1680 to throw out the Spanish oppressors.
When the Spanish returned in 1692, their rule was significantly less harsh. However, the Spanish brought horses into the New World and as the number of Spanish increased, so did the number of horses. That brought more and more raids from the Comanches as they came for horses and whatever else they could carry away. The Comanches were finally subdued by Governor Juan Bautista de Anza in 1776 but by then, the impact of European diseases was being strongly felt. A smallpox epidemic in the late 1820s virtually ended the making of pottery at Nambé.
Photo courtesy of John Phelan, Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported License
About Bowls
The bowl is a basic utilitarian shape, a round container more wide than deep with a rim that is easy to pour or sip from without spilling the contents. A jar, on the other hand, tends to be more tall and less wide with a smaller opening. That makes the jar better for cooking or storage than for eating from. Among the Ancestral Puebloans both shapes were among their most common forms of pottery.
Most folks ate their meals as a broth with beans, squash, corn, whatever else might be in season and whatever meat was available. The whole village (or maybe just the family) might cook in common in a large ceramic jar, then serve the people in their individual bowls.
Bowls were such a central part of life back then that the people of the Classic Mimbres society even buried their dead with their individual bowls placed over their faces, with a "kill hole" in the bottom to let the spirit escape. Those bowls were almost always decorated on the interior (mostly black-on-white, color came into use a couple generations before the collapse of their society and abandonment of the area). They were seldom decorated on the exterior.
It has been conjectured that when the great migrations of the 11th, 12th, 13th and 14th centuries were happening, old societal structures had to change and communal feasting grew as a means to meet, greet, mingle with and merge newly arrived immigrants into an already established village. That process called for larger cooking vessels, larger serving vessels and larger eating bowls. It also brought about a convergence of techniques, styles, decorations and design palettes as the people in each locality adapted. Or didn't: the people in the Gallina Highlands were notorious for their refusal to adapt and modernize for several hundred years. They even enforced a No Man's Land between their territory and that of the Great Houses of Chaco Canyon, killing any and all foreign intruders. Eventually, they seem to have merged with the Towa as those people migrated from the Four Corners area to the southern Jemez Mountains.
Traditional bowls lost that societal importance when mass-produced cookware and dishware appeared. But, like most other Native American pottery in the last 150 years, market forces caused them to morph into artwork.
Bowls also have other uses. The Zias and the Santo Domingos are known for their large dough bowls, serving bowls, hair-washing bowls and smaller chili bowls. Historically, these utilitarian bowls have been decorated on their exteriors. More recently, they've been getting decorated on the interior, too.
The bowl has also morphed into other forms, like Marilyn Ray's Friendship Bowls with children, puppies, birds, lizards and turtles playing on and in them. Or Betty Manygoats' bowls encrusted with appliqués of horned toads or Reynaldo Quezada's large, glossy black corrugated bowls with custom ceramic black stands.
When it comes to low-shouldered but wide circumference ceramic pieces (such as many Sikyátki-Revival and Hawikuh-Revival pieces are), are those jars or bowls? Conjecture is that the shape allows two hands to hold the piece securely by the solid body while tipping it up to sip or eat from the narrower opening. That narrower opening, though, is what makes it a jar. The decorations on it indicate that it is more likely a serving vessel than a cooking vessel.
This is where our hindsight gets fuzzy. In the days of Sikyátki, those potters used lignite coal to fire their pieces. That coal made a hotter fire than wood or manure (which wasn't available until the Spanish brought it). That hotter fire required different formulations of temper-to-clay and mineral paints. Those pieces were perhaps more solid and liquid resistant than most modern Hopi pottery is: many Sikyátki pieces survived intact after being slowly buried in the sand and exposed to the desert elements for hundreds of years. Many others were broken but were relatively easy to reassemble as their constituent pieces were found all in one spot and they survived the elements. Today's pottery, made the traditional way, wouldn't survive like that. But that ancient pottery might have been solid enough to be used for cooking purposes, back in the day.
About Fire Clouds
Fire clouds are a product of the firing process. They are generally random darkenings of a piece where it was touched by a wayward plume of smoke and the clay absorbed some of the carbon in it. Conversely, in an oxygen-reduction atmosphere (which is how Tewa potters turn their otherwise red pieces black), surfaces randomly exposed to open air don't turn as black while surfaces protected from exposure to the oxygen-reduction atmosphere turn red. In some pueblos, the appearance of fire clouds is a testament to the lack of experience of the potter. In others it's a testament to the greater experience of the potter.
Dineh potters often stack their firewood in ways to generate fire clouds on their brown clay as that may be the only decoration on the piece.
Fire clouds on Hopi pottery are usually seen as a darker blush on an otherwise yellow piece. That is a result of their yellower clay and their use of cedar bark and sheep manure for firing. Franklin Tenorio of Santo Domingo also often used cedar bark to fire his pieces but he liked to make his surfaces look smudged and smoky by partially blocking the air flows around his fires. In contrast, his cousin Thomas Tenorio prefers to fire his pieces inside a metal container that denies any entrance to fire-cloud generating smoke or atmosphere.
Potters who work with micaceous pottery also work with fire clouds. When firing in a free-oxygen atmosphere, fire clouds may be the only decoration on a piece. When firing in an oxygen-reduction atmosphere to produce a black piece, "fire clouds" are any lighter areas left on the surface after the firing is complete.






