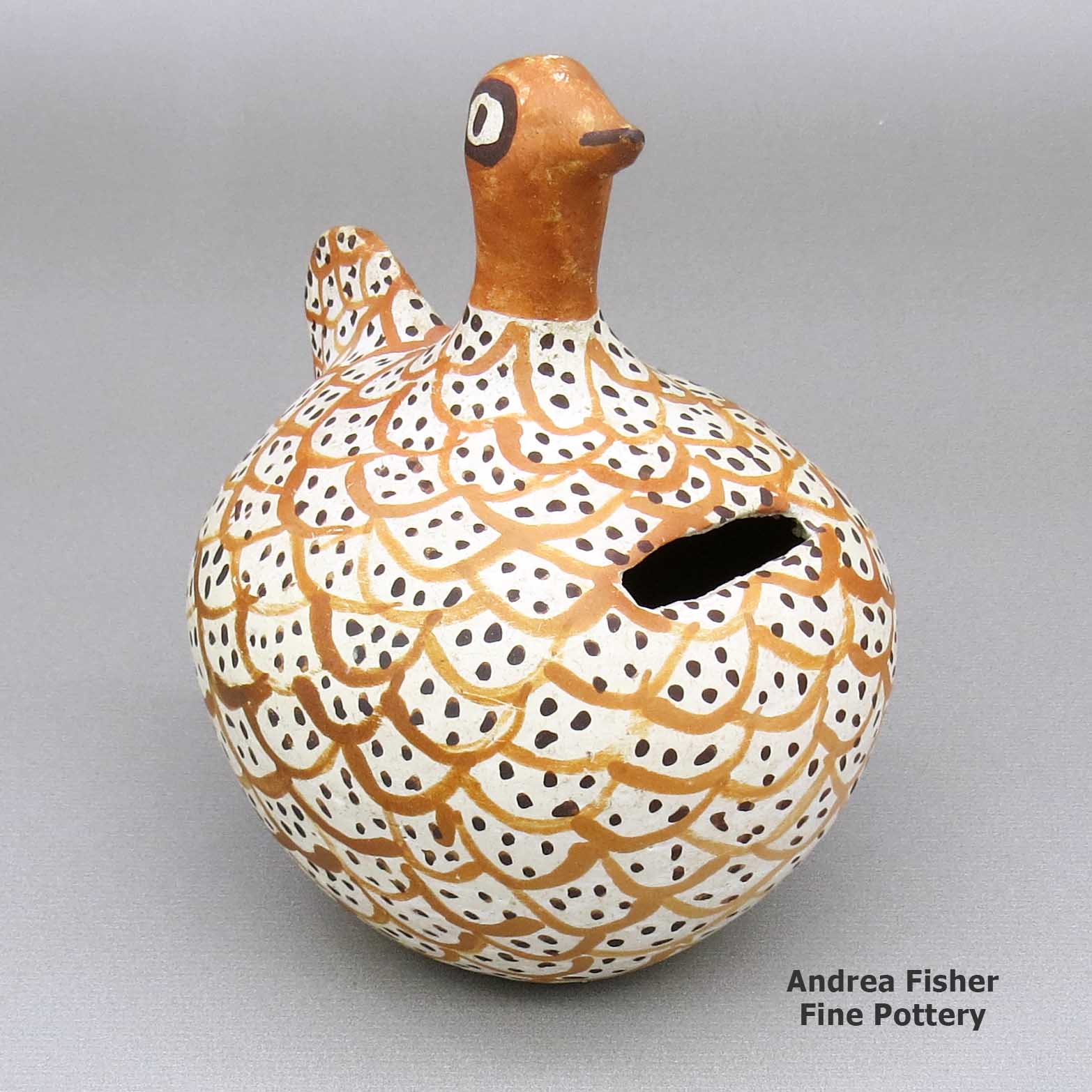
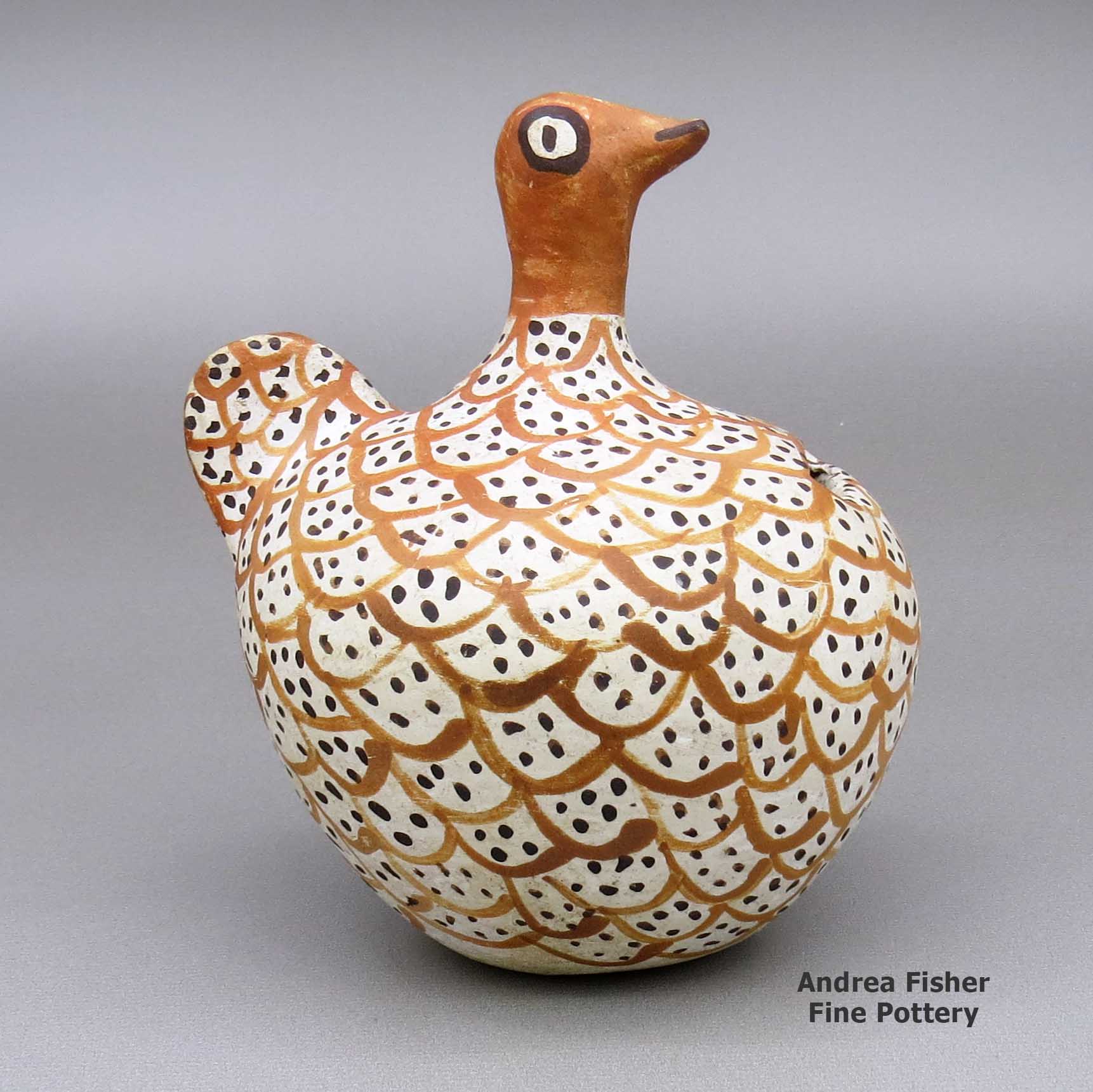
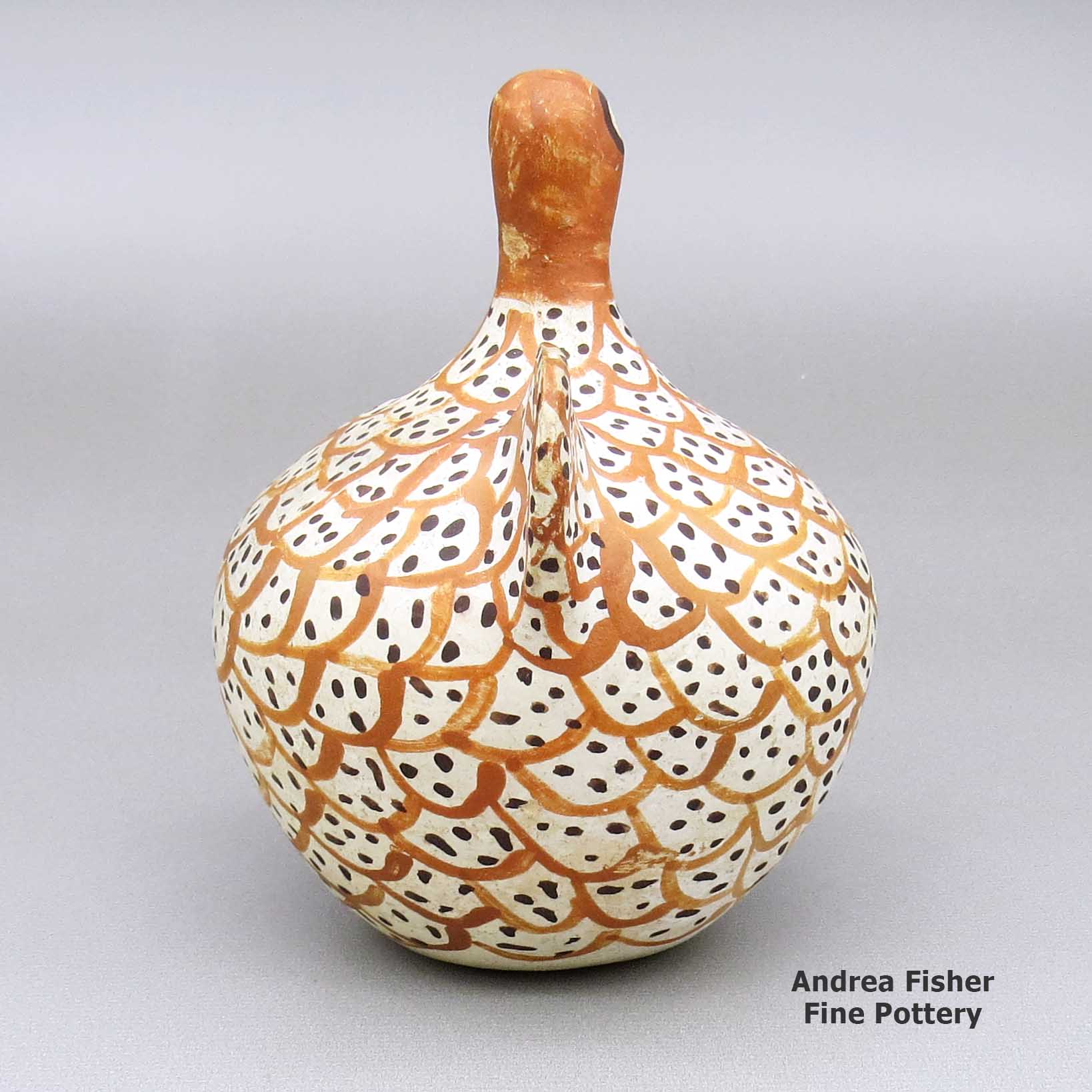
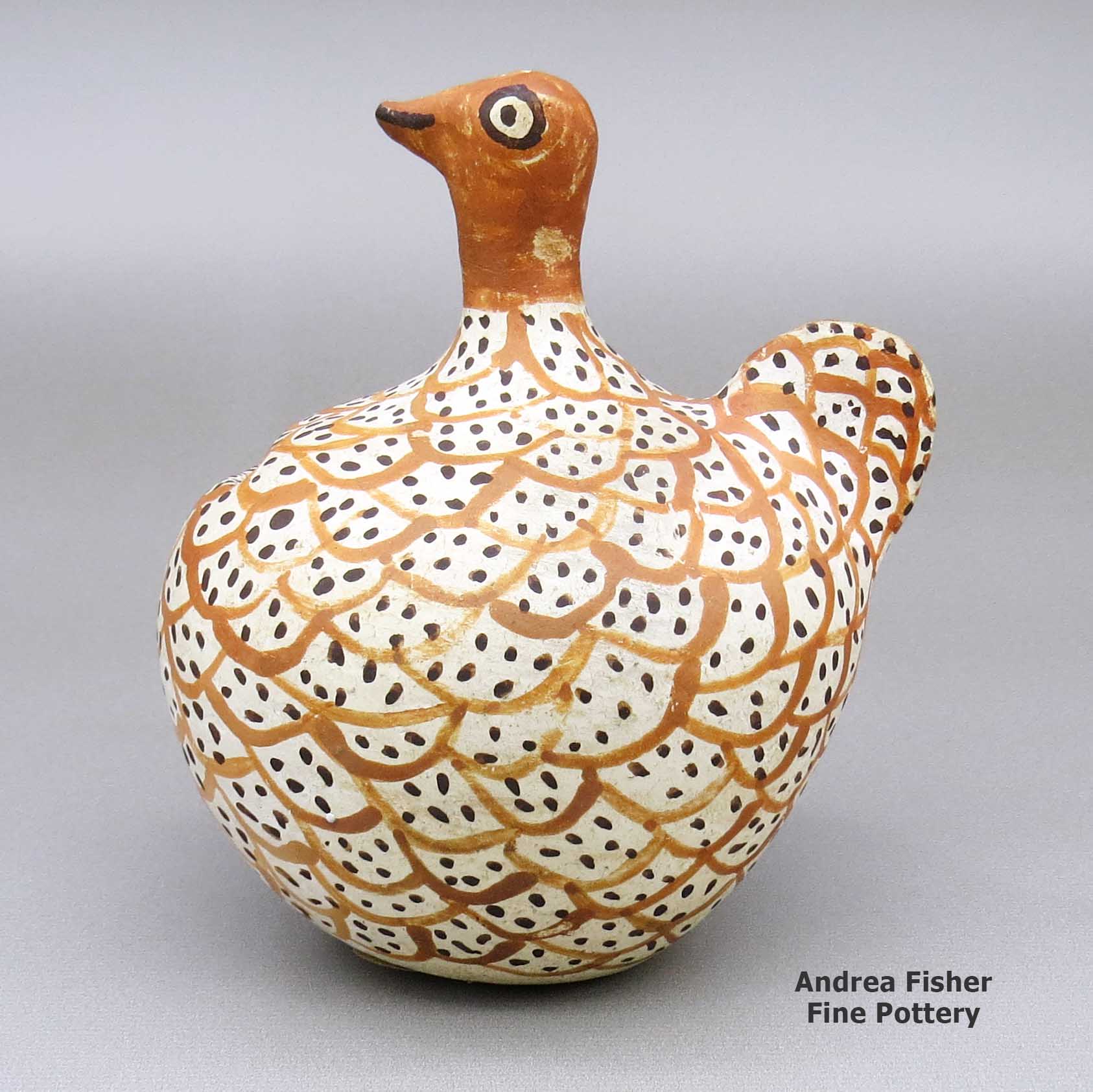
| Dimensions | 4.25 × 3.5 × 4.75 in |
|---|---|
| Signature | Acoma N.M. |
Unknown Acoma Potter, zzac2m530, Polychrome bird coin bank
$115.00
A polychrome bird figure coin bank decorated with a bird element design
In stock
Brand
Unknown Acoma Potter
A Short History of Acoma Pueblo
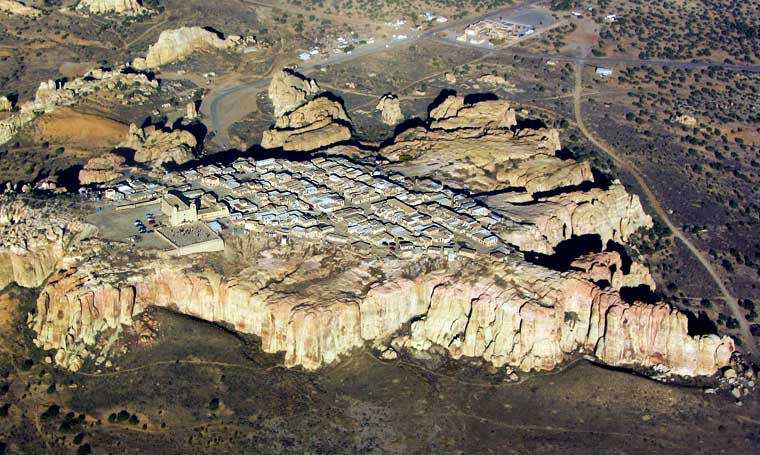

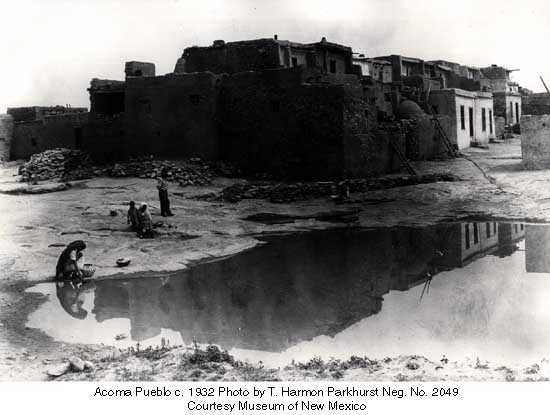
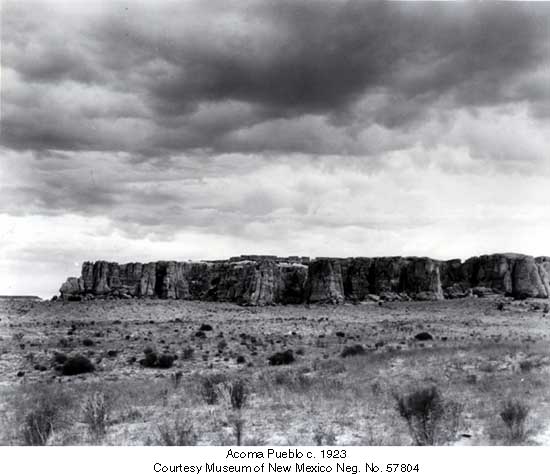
According to Acoma oral history, the sacred twins led their ancestors to "Ako." Ako turned out to be a magical mesa composed mostly of white rock. There the sacred twins instructed the ancestors to make that mesa their home. Acoma Pueblo is called "Sky City" because of its position atop the high mesa.
Acoma, Old Oraibi (at Hopi) and Taos all lay claim to being the oldest continuously inhabited community in the U.S. Those competing claims are hard to settle as each village can point to archaeological remnants close by to substantiate each village's claim. Acoma is located about 60 miles west of Albuquerque in a landscape littered with the ruins of ancient pueblos, many more than 1,000 years old.
The people of Acoma have an oral tradition that says they've been living in the same area for more than 2,000 years. Archaeologists feel more that the present pueblo was established near the end of the major migrations in the 1200 and 1300s. The location is essentially on the boundary between the Mogollon (Mimbres), Hohokam (Salado) and Anasazi (Ancestral Puebloan) cultures. Each of those cultures has had an impact on the styles and designs of Acoma pottery, especially since modern potters have been getting the inspiration for many of their designs from pot shards they have found while walking on pueblo lands.
Francisco Vasquez de Coronado ascended the cliff to visit Acoma in 1540. He afterward wrote that he "repented having gone up to the place." But the Spanish came back later and kept coming back.
Around 1598 relations between the Spanish and the Acomas took a nasty turn with the arrival of Don Juan de Oñaté and the soldiers, settlers and Franciscan monks that accompanied him. After making the arduous ascent to the mesa top, de Oñaté decided to force the Acomas to swear loyalty to the King of Spain and to the Pope. When the Acomas realized what the Spanish meant by that, a group of Acoma warriors attacked a group of Spanish soldiers and killed 11 of them, including one of de Oñaté's nephews.
De Oñaté retaliated by attacking the pueblo. His troops burned most of it and killed more than 600 people. Another 500 people were imprisoned by the Spanish. Males between the ages of 12 and 25 were sold into slavery. 24 men over the age of 25 had their right foot amputated. Many of the women over the age of 12 were also forced into slavery. Most were parceled out among Catholic convents in Mexico City.
Two Hopi men were also captured at Acoma. The Spanish cut one hand off of each and sent them home to spread the word about Spain's resolve to subjugate the inhabitants of Nuevo Mexico. Spanish monks did make the trip a few years later but Spanish military made hardly an appearance in Hopiland.
When word of the massacre (and the punishments meted out after) got back to King Philip in Spain, he banished Don Juan de Oñaté from Nuevo Mexico. Some Acomas had escaped that fateful Spanish attack and returned to the mesa top in 1599 to begin rebuilding.
In 1620 a Royal Decree was issued which established civil offices in each pueblo and Acoma got its first governor. That didn't help the people any as those appointed to the government positions were also those most on the take with the Spanish authorities. By 1680, the situation between all of the pueblos and the Spanish had deteriorated to the point where the Acomas were extremely willing participants in the 1680 Pueblo Revolt.
After the successful Pueblo Revolt pushed the Spanish back to Mexico, refugees from other pueblos began to arrive at Acoma. Most feared the eventual Spanish return and probable reprisals. That strained the resources of Acoma badly. Then the Spanish returned in force and residents of the pueblo had to make a hard decision. Many of the refugees chose to try a peaceful solution: they relocated north to the ancient Laguna area and made peace with the Spanish as soon as they reappeared in the region. Acoma held out against the Spanish for awhile but soon capitulated.
Over the next 200 years, Acoma suffered from breakouts of smallpox and other European diseases to which they had no immunity. At times they would side with the Spanish against nomadic raiders from the Ute, Apache and Comanche tribes. Eventually New Mexico changed hands. Then the railroads arrived and Acoma became dependent on goods made in the outside world.
For many years the villagers were content on the mesa. Now most live in villages on the valley floor where water, electricity and other necessities are easily available. A few families still make their permanent home on the mesa top. The old pueblo is used almost exclusively these days for ceremonial celebrations.

For more info:
Acoma Pueblo at Wikipedia
Pueblo of Acoma official website
Pueblos of the Rio Grande, Daniel Gibson, ISBN-13:978-1-887896-26-9, Rio Nuevo Publishers, © 2001
Acoma & Laguna Pottery, Rick Dillingham with Melinda Elliott, ISBN 0-933452-32-2, School of American Research Press, © 1992
Upper photo courtesy of Marshall Henrie, Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported License
About Western Keresan Designs
Those of the Western Keres tradition have a plethora of traditional designs. A reason for that is they have occupied a region on the boundary between the Mogollon cultures to the south and the Ancestral Puebloan cultures to the north. And some of them have been living and working in the same place for a thousand years or more. They have also been making and breaking pottery the whole time. The area of Laguna has been more or less populated for a similar amount of time and, when populated, the Lagunas have moved around more than the Acomas.
Because Acoma and Laguna are located in that boundary area between Chaco Canyon influence to the north and Mogollon-Mimbres Valley influence to the south, designs and techniques have been coming and going across the landscape for many years. Over time, broken potsherds covered with multiple designs have fallen to the ground almost everywhere, just waiting to be picked up by someone, have their designs copied and revived, and their most basic constituents ground and mixed with fresh clay and to be reborn as pots again.
In the 1950s, that started happening a lot, potsherds being picked up and their designs revived, that is. Many of those designs have since been traced back to artisans in the Mimbres Valley working before 1150 CE. They had a unique perspective on the birds, animals, insects and people of their world, and used that perspective to draw and paint unique patterns. Many of those patterns are still being recreated on pottery across the Pueblo world, but especially at Acoma and Laguna. Central to the design palette are stories from the adventures of the Twin Warriors. While some Flower World iconography is also present in the Acoma design palette, there is extremely little from the kachina cults of the Hopi and Zuni.
One of the more recent "traditional" Acoma designs is the parrot holding a twig with berries in its claws. Often there is a rainbow above or below the parrot. Parrots are not natural in New Mexico, they had to have been imported. Before about 1450 CE, there was a trade in parrots and macaws through Paquimé to regions in the north. The remains of macaws have been pretty common but the remains of green parrots have only been recovered from three pueblos: Cicuyé, Paquimé and Grasshopper Pueblo in Arizona. The ancient-most Acoma parrot design has a Mimbres/Mogollon heritage while the parrot most painted today looks more like it came from an Amish trader's box. And it likely did.
With the arrival of Spanish colonists in New Mexico, pueblo potters changed their pottery to meet the demands of a new market. Their shapes and designs changed with that. Everything changed again with the arrival of Amish traders with their enameled cookware in the 1850s. The "new" Acoma parrot was pictured on the boxes those pots came in. The parrot came into being around 1880 and has been in use so long now it is considered "traditional."
Pottery was always in production at Acoma but from about 1600 to about 1950, it was heavily influenced by colonial shapes and designs. Eventually, the potters were reduced to producing items for the tourist trade to make ends meet, and that didn't go over so well either. Their own interest in making pottery fell off. Lucy Lewis, Jessie Garcia and Marie Z. Chino started decorating their pieces with their new interpretations of ancient Mimbres, Tularosa and Cibola designs in the 1920s and interest, both outside and inside the pueblo, grew again from there.
Laguna was impacted more heavily by the newcomers. Two Methodist missionaries married women in the pueblo and one of them shortly had himself elected President of the Pueblo. One of the first things he did was order the destruction of all the kivas on Laguna Pueblo land. That caused a schism and many Lagunas relocated to Isleta for a number of years (some of them are still there).
The Southern branch of the Transcontinental Railroad ran across Laguna Pueblo, and offered jobs to many of the men. That essentially ended the making of pottery by most tribal members. Then uranium was discovered under pueblo lands and more men went to work mining for that. Only a couple families passed the traditional knowledge down, until it eventually reached Evelyn Cheromiah. Nancy Winslow, an Anglo woman from Albuquerque, helped Evelyn obtain a grant to teach pottery making on the pueblo and a small revival started from there. Laguna potters, too, work their designs from designs they find on potsherds they find lying on the ground around the old pueblos. Their designs are very much like those of Acoma, usually just with more white space and bolder lines.
About Figures and Figurines
Generally, "Figure" denotes a real or mythic creature, like an owl or human or katsina or Corn Maiden. Whether form or decoration, all Puebloan pottery figures are meant to invoke particular spiritual essences. That's why "effigy" is used almost as often as "figure" to denote these pieces.
Among most Puebloans, the figure of an owl, for example, signifies all the physical and spiritual aspects attributed to the owl. It's a form of prayer to the spirit of "Owl" and the appropriately decorated physical form is meant to make that spirit manifest. However, to the Zuni people an owl is a good omen and to the Tewa people, an owl is a bad omen. Some potters at Santa Clara have made owls anyway, they just shaped and decorated them to reflect that "badness."
That explanation may make more sense in the case of the Corn Maiden as she is a mythic entity whose existence revolves around the most ubiquitous food staple in the Puebloan world: corn (maize). All representations of the Corn Maiden are meant to invoke her benevolence and abundance for their people. Because of her mythical/spiritual nature, different pueblos have slightly different physical forms for her but they all incorporate the basic form of a female human face on an ear of corn.
The potters of Tesuque turned out thousands of muna figures (also known as rain gods)for several decades, until they virutally burned out their pottery tradition. These muna had very specific shapes but were decorated with everything from micaceous slips to incised lines to polychrome geometric designs to poster paints. They were also made purely for domestic American consumption, sometimes delivered by the barrel to be used as prizes and giveaways.
The Storyteller is another figure based on Puebloan tradition: a tribal elder singing the stories of the tribe's oral history to the children. The original was based on the traditional cultural story: a grandfather singing his part of the story in his native language so the children learn both the language and their identity against the backdrop of that history. Shortly, the storyteller form was duplicated in several other pueblos, each pueblo's potters adapting the form to their local situation. In some places, the grandmother became the primary sex of their storytellers. At Jemez, that responsibility was shared between grandmothers and grandfathers. Then some potters in search of new niches in the marketplace branched into making "spirit figure" storytellers, like eagles, ravens, hummingbirds, cats and dogs. Some Zuni potters have made storyteller owls.
Similar to the Storyteller is the Story Time: a set of separate children displayed around a larger central singing figure.
The Nativity set (also known as nacimiento) is a set of figures based on the intersection of Puebloan mythologies and stories they heard from Christian missionaries. Those potters who make them also tend to favor dress, shapes and designs that reflect their own heritage(s). The first few nativities made at Tesuque Pueblo were decorated with Spanish colonial costumes but that soon changed and every nativity made since has a distinct blend of Native American and Christian, with no other reference to colonialism. The "Singing Angel" (a single standing figure with outstretched wings and hands clasped together in prayer) and "Flight to Egypt" (usually depicting Mary with a baby Jesus on the back of a donkey and a standing Joseph nearby holding the rein) are similar mixes of tribal and Christian figures. The miniature nativities made by Santa Clara/Dineh artist Linda Askan clearly show Dineh religious influence in the headresses worn by Joseph, the angel and the three wise men. At the same time, the Dineh Folk Art nativities made by Jonathan Chee are based on the realities of daily Dineh life: the three wise men wear wide-brim hats and blue jeans, and bring gifts of salt and 50-pound bags of flour.
Pueblo and Dineh artists also make a full zoo of domesticated, farm and wild animal figures: horses, donkeys, cows, chickens, pigs, sheep, turkeys, giraffes, elephants, dogs, cats, mermaids, women-dressed-up-and-taking-selfies and cowboys among them.
About Bird Elements
One of the main tenets of the Flower World ideology is that birds are messengers to and from Paradise. They carry our prayers to Heaven and they bring back the responses. Not all the pueblos accepted the Flower World ideology but it seems almost everyone, almost everywhere, agrees that birds are the messengers of Heaven. All pueblos do have multiple designs that incorporate feathers, if feathers aren't the main element of the design.
The Flower World ideology originated in central Mexico and most likely traveled north to the pueblos in the company of missionaries and long-distance traders. Turquoise was taken south while tropical birds, copper bells, seashells, and textiles (with particular spiritual designs on them), along with other spiritual items, were taken north. Going either way, almost everyone passed by Paquimé. The trade routes from the south came together there and the trade routes to the north diverged from there. That business didn't really come together until the first structures went up in the immediate vicinity of Paquimé, around 1150 CE. Then it ended around 1450 CE when the city was abandoned. That was also the end of pilgrims making their way south and then coming north again a few years later. For more than 300 years that traffic had been a major profit center and prestige generator for the people of Paquimé and Casas Grandes. After Paquimé was abandoned, though, the trade and pilrimage routes became far more dangerous. With the advent of the Aztec Empire in central Mexico, being a foreigner in that area became far more dangerous, too. Essentially, the puebloans who had embraced the Flower World ideology were cut off from their Holy Land.
The Flower World Complex, with its symbology, flowed across the American Southwest and eventually reached the Four Corners area. But it arrived at about the same time the kachina cults were coming together and the people were abandoning the Four Corners. The Flower World ideology was felt to be greater than what had come before so it's symbology was basically imprinted on top of that. Then the designs of the kachina cults and other clans were added on top of the Flower World symbology. Then came the Europeans with their designs and spiritual practices.
One of the principals of Native American design is that it is necessary only to note one part of most animals to imply the presence of the whole, especially when it comes to birds and bird elements. A lot of the design on Hopi pottery can only be described as "bird elements," although it is often possible to discern parrot feathers from eagle feathers, and eagletails from other bird's tails.
The Zunis have an ancient "almost-spiral" design that comes from the beaks of their equally ancient "rainbirds." The Zunis also like to make owl figures as owls are a symbol of wisdom to them. To some Northern Tewas, owls are creatures to be feared.
At Acoma they have a "cloudeater," a crane pictured with neck bent over and filling with fish shown sideways in its throat as it swallows them whole. Acoma potters also have a parrot that resembles the parrot found on the sides of the boxes carried by Amish traders back in the day. The parrot is not complete without a branch with leaves, and maybe berries, in its claws.
At Santo Domingo, religious dictates limit what can be imaged on pottery offered to the public. Birds, fish, turtles and flowers are allowed, along with a vast catalog of geometric designs. Images of humans are not. Next door at Cochiti, almost anything goes
The artists of the Mata Ortiz area are resurrecting some of the designs left behind by artists of old but they have no inner connection with the Flower World. Others in today's Mata Ortiz have gone totally contemporary: carving, scratching and painting beautiful images of birds with branches, vines and flowers.