| Dimensions | 5.75 × 3.5 × 3.75 in |
|---|---|
| Condition of Piece | Very good, normal wear |
| Date Born | 2000 |
| Signature | Agnes Peynetsa Zuni NM, with copyright symbol |
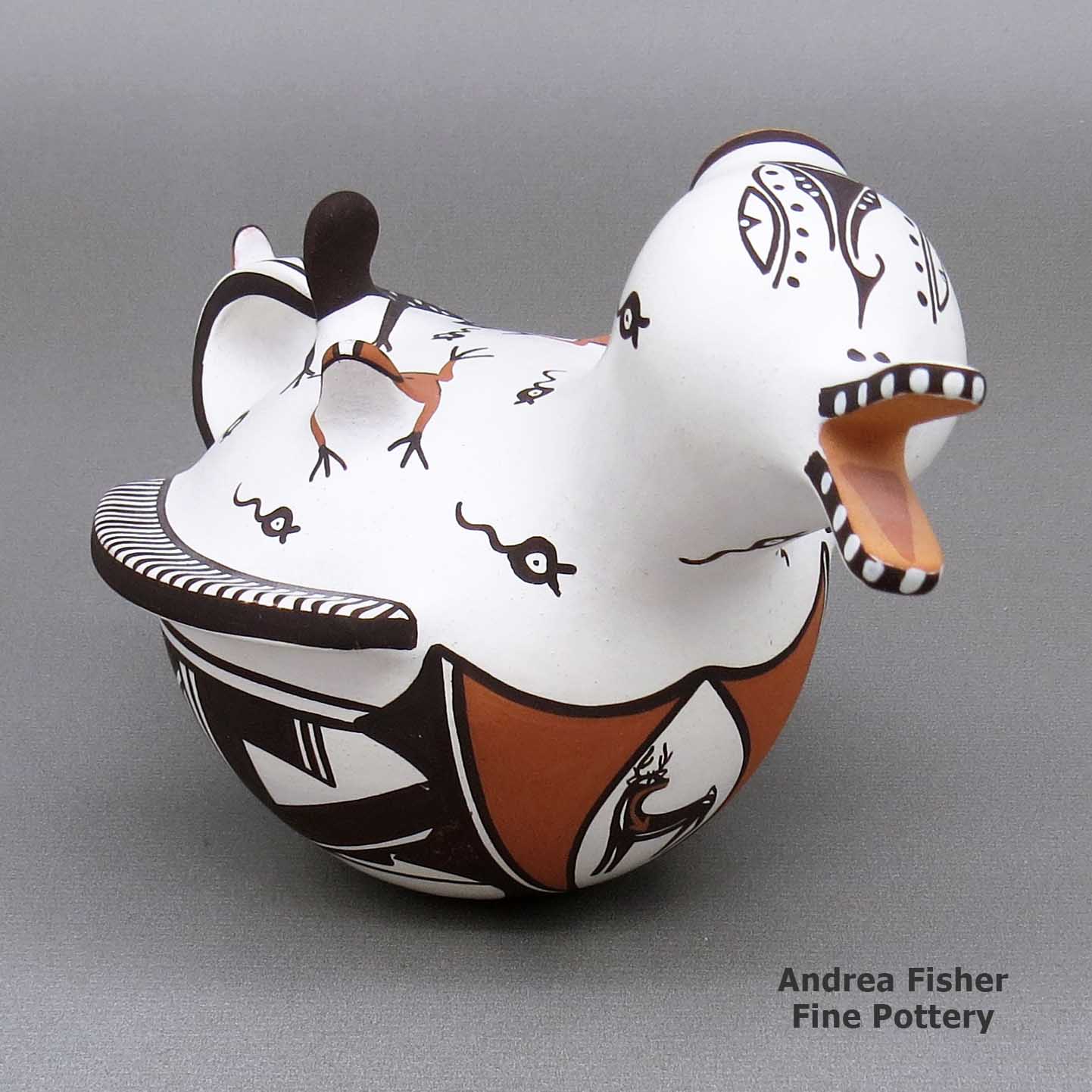
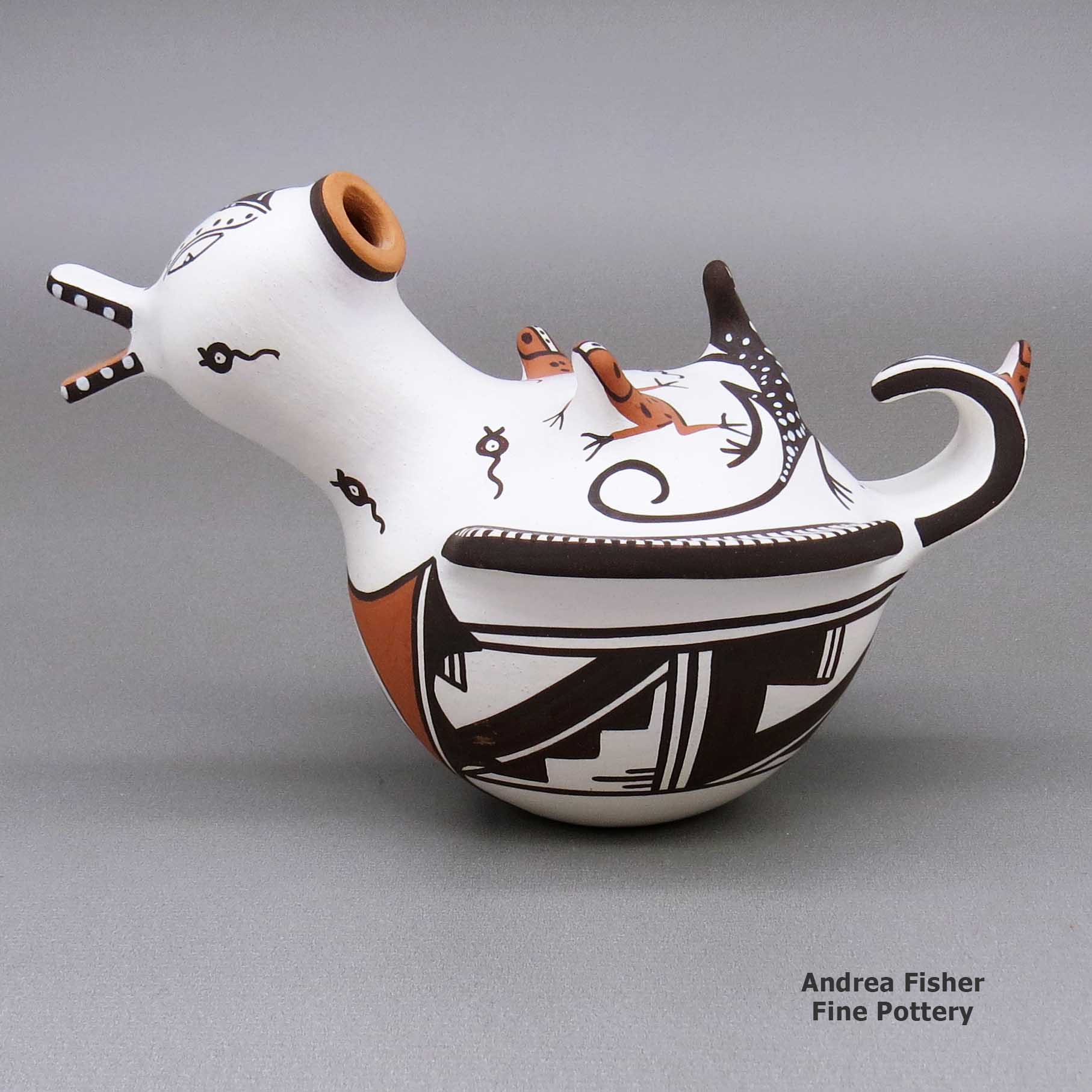
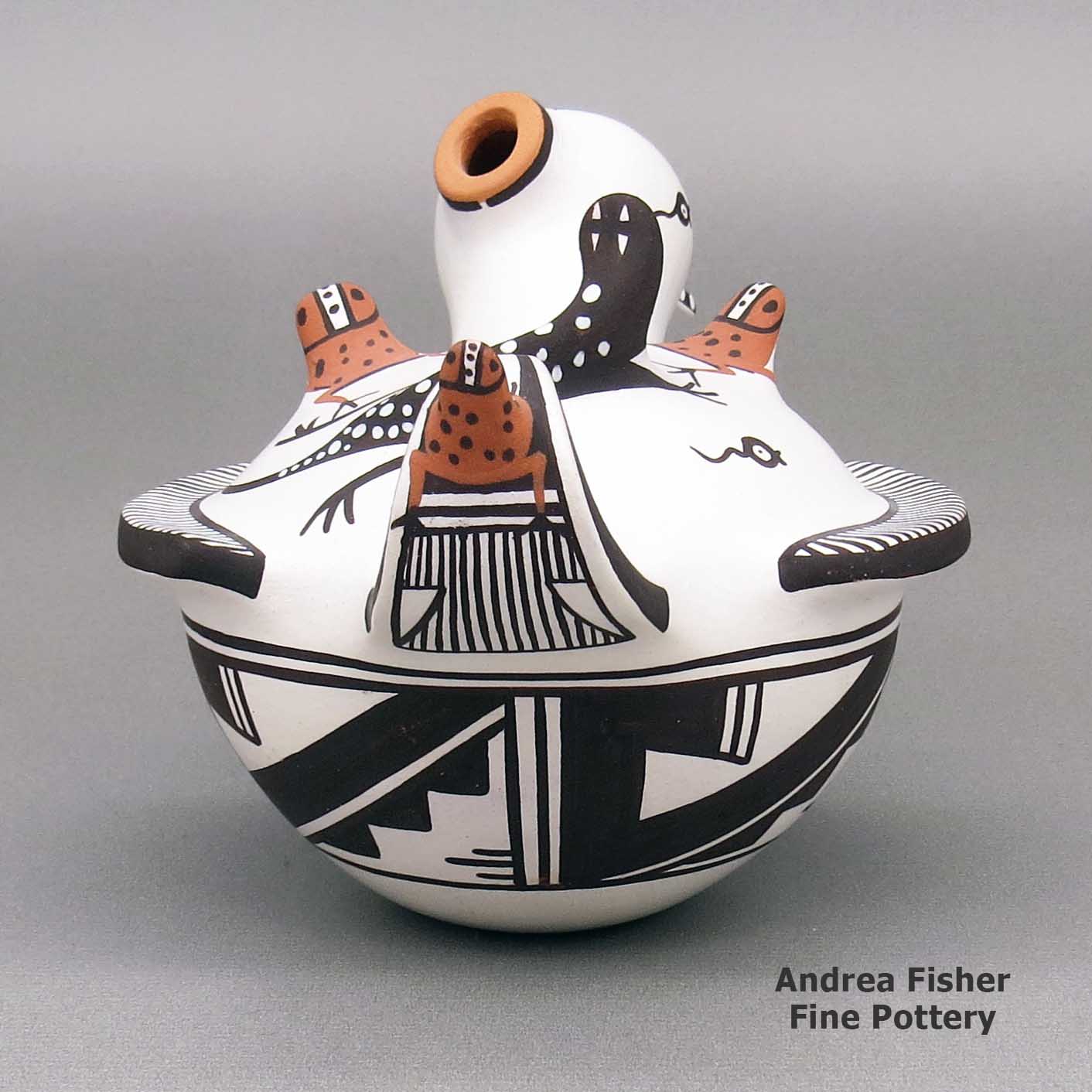
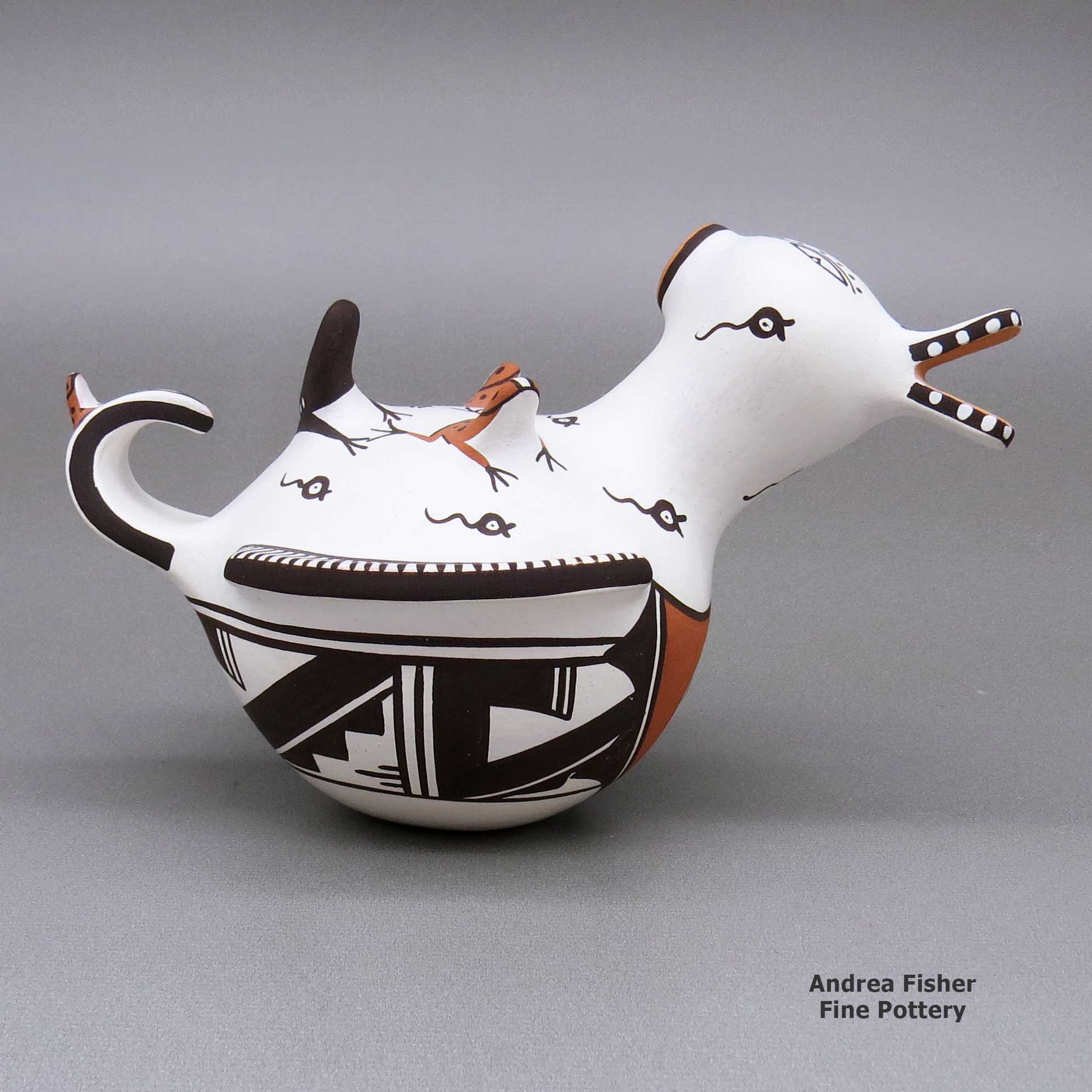
Agnes Peynetsa, zzzu3b515, Duck pot with a deer with heart line design
$395.00
A polychrome duck pot decorated with an applique-and-painted deer-with-heart-line, tadpole, frog, lizard and geometric design
In stock
- Product Info
- About the Artist
- Home Village
- Design Source
- About the Shape
- About the Design
- Teaching Tree
Brand
Peynetsa, Agnes
Jennie taught the making of pottery in mostly traditional ways – mostly traditional because the school had an electric kiln and she used it in her classes. So when the students left high school, they no longer had access to that kiln…
However, breaking this rule were Agnes' brother Anderson Peynetsa and their sister Priscilla Peynetsa. Once she finished school, Agnes at first worked with and learned from Anderson. Anderson built a very respectable body of work in the mid-1990s and established himself as one of Zuni's premier potters. Many of Anderson and Agnes's older, combined effort works are signed "A.A. Peynetsa".
When Anderson married Avelia, "A.A. Peynetsa" came to mean Anderson and Avelia. Agnes was then on her own.
Early in her career, Agnes also worked with Berdel Soseeah. Priscilla also worked hard and became one of Zuni's finest and most recognized potters.
Agnes digs her own clay locally, grinds it, cleans it, and then forms the pot completely by hand. She also grinds her own slip for the decoration and makes her own paint. However, like most Acoma and Zuni potters these days, she uses an electric kiln.
Defending the use of the electric kiln, the brilliant potter Noreen Simplicio stated in Milford Nahohai's and Elisa Phelp's Dialogues with Zuni Potters: "Over at [Santa Fe] Indian Market, when you try to enter your work, they'll downgrade it because it's fired in a kiln. I think it's good that they have that for people who are totally traditional, but they should have room for people that, like myself, are both traditional and contemporary."
Agnes is both traditional and contemporary in her pottery. According to Allen Hayes and John Blom's "Southwestern Pottery - Anasazi to Zuni": "All Peynetsa work is excellent: excellently decorated, excellently sculpted, often with a quiet sense of humor, never with an inflated sense of importance. Where else can you see major, museum-quality pieces right alongside a refrigerator magnet, all done with the same loving care?"
In 2018 at the Heard Museum Guild Indian Fair & Market, Agnes earned a Judge's Award from Betsy Fahlman, PhD. It was awarded for artwork entitled: "Water jar".
A Short History of Zuni Pueblo

"K'ynánas'tipe stretched his legs to the four great seas, then gradually he settled down and called out, 'where my heart and navel rest, beneath them mark the spot and build your town there for that shall be the midmost place of Mother Earth.' As he squatted over the middle of the plain and the valley Zuni, he drew in his legs and his feet marked the trails leading outward like the radiating web of a spider. The fathers of the people built on this spot and rested their fetishes there." - Frank H. Cushing, Outlines of Zuni Creation Myths, pp. 428-9
Archaeologists have dated some sites on the Zuni Reservation back to the Paleo-Indian Period, more than 4,500 years ago. During the Archaic Period (2,500 BCE to 0 CE), the forebears of the Zuni were hunter-gatherers and just beginning to develop agriculture. The Basketmaker Period (0 CE to 700 CE) saw agriculture become more developed and the Zunis make their first pottery. The Pueblo I Period (700 CE to 1100 CE) saw an expansion of the population and larger settlements were built in the Zuni River area along with the development of the first painted Zuni pottery.
The Pueblo III Period (from 1100 to 1300 CE) saw further population growth in the Zuni River area and a shift from small houses to larger, plaza-oriented villages. The Pueblo IV Period (1300 to 1500 CE) was the time of significant bad weather, great drought and the beginning of the flood of Athabascans and Utes. Many tribal groups were forced out of the Four Corners area and relocated to locations near the Rio Grande, Rio Puerco, Zuni River and Little Colorado River. The main Zuni Pueblo was founded during this time but there were several other large villages in the area, too.
In 1540 Francisco Vasquez de Coronado arrived at the gates of Hawikuh, at the time one of the larger of seven Zuni pueblos. He first approached the pueblo at the end of a four-day religious festival. The Zuni chief had spilled a line of corn meal across the ground before the entrance to the pueblo, meant to signify to the Spanish that they shouldn't cross the line and enter the village yet. Coronado interpreted that line of corn meal as an act of war and immediately ordered his soldiers to attack.
Coronado was almost killed in the fighting (Zuni warriors had dropped a large rock on him, knocking him off his ladder and almost crushing him) but his soldiers did finally win the battle. As Coronado and his men brought horses and sheep with them, they were probably the first such livestock the Zunis had ever seen. The gold the Spaniards were looking for: it turned out to be Sikyátki Polychrome bowls and jars, yellow clay gifts from the Hopi people to the Zuni people.
The Zuni chief did give Coronado a refugee from the Plains tribes, someone who'd somehow made his way as a lone traveler to Hawikuh. That refugee was supposed to be a guide for Coronado and his men but he was instructed by the Zuni chief to take Coronado into the Plains and get him lost there. When Coronado finally realized that, more than a year later, he ordered the guide executed, then turned his men around and headed back to Zuni and Mexico.
When he passed by Zuni in 1542, Coronado left three Mexican Indians behind with the tribe. They most likely informed the tribal leaders of the extent of the Spanish domain in Mexico and the power they exercised there.
Except for a couple passing exploratory expeditions, the Zuni pueblos were left alone until the 1620s. Then came the friars who oversaw the construction of a mission church at Hawikuh in 1629. At first the Zuni people were friendly with the priests but with the forced labor requirements and forced religious conversions, the priests wore that welcome out quickly. Relations had changed drastically for the worse by the time of the Pueblo Revolt of 1680. Zuni warriors killed the priests and burned the missions but they preserved the relics and icons the priests had brought from Spain.
The tribe built a village near their fortress atop Dowa Yalanne and prepared to defend their people and way of life against the Spanish army. When Don Diego de Vargas arrived with troops in 1692, he attacked the fortress twice and failed. Then he negotiated with the Zuni war chief and was allowed to ascend to the top of Dowa Yalanne. He was given a tour of the property and he found many relics from the destroyed missions there. With that knowledge, he arranged a peace between the Spanish and the tribe. Between 1693 and 1700 the tribe consolidated all their small villages into what is now the Pueblo of Zuni.
Photo courtesy of Ken Lund, Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike License 2.0 Generic
Traditional Zuni Designs
Anthropologists say the Zuni people have been isolated for so long, there are no referrents to where their language came from. The images they paint on pottery, though, show some signs of cross-pollination with the Hopi, Acoma, Laguna and some of the Rio Grande pueblos.
Among those images are the heart-line, as in deer-with-heart-line. At some pueblos, that has become bear-with-heart-line and antelope-with-heart-line. Sometime around 1890, a Laguna potter made the journey to Zuni to learn from a potter there how to make better pottery. He stayed only a few months before returning to Laguna, via Acoma. He brought back better knowledge of mixing the clay, making the paints and painting the designs. Among those designs was the deer-with-heart-line.
At the time of first Spanish contact, there were seven Zuni pueblos spread out along the Zuni River. By about 1720, that was reduced to one. When the American archaeologists arrived, they set about excavating almost every abandoned village they could find. In the process, many pieces of ancient pottery came to light. That's where the names Matsaki Polychrome and Red-on-buff (matte paint on white and red slips, produced from about 1375 CE to about 1700 CE), Kwakina Polychrome (glaze paint on a white slip, produced from about 1325 to about 1400) and Heshotauthla Black-on-red and Polychrome (glaze decorations, produced from about 1275 to about 1400) came from. A primary difference between Kwakina and Heshotauthla designations is the color the inside of the bowl is slipped with. The decorations on both are painted with lead glaze colors and are taken from the same design library, which includes many designs common to the Mogollon Highlands in eastern Arizona (such as St. Johns Polychrome), although the designs tend to be not as well executed.
The advent of Matsaki Polychrome and Red-on-buff coincides with the entrance of an immigrant community from the north: the land of the Hopi. With them came the basic design library of what we now refer to as "Sikyatki Polychrome." Production of Kwakina- and Heshotauthla-style pottery dropped off quickly after the arrival of those who produced the Matsaki styles. It was around that time, too, that the Zuni villages around the Zuni Mountains were abandoned and the people pulled back to the pueblos along the lower Zuni River.
After Spanish contact and conquest, the Zunis were reduced to about one-tenth their population by Spanish diseases and labor practices. Before too long, they were gathered together in one village near the bank of the Zuni River. Their image catalog changed, too. When the American archaeologists and ethnologists came, they removed virtually every artifact of Zuni history they could dig up or find otherwise. Then they spirited it all away to storerooms on either coast, where most of it remains in boxes in dingy basement rooms today.
In 1986, Josephine Nahohai and several members of her family traveled to Washington DC and explored the basement storage shelves of the Smithsonian Institute, copying every ancient Zuni shape and design they found into their notebooks. When they returned to Zuni, their drawings became the basis for many of what are now referred to as traditional Zuni designs. Among those designs are symbols for mountains and forest, and images of frogs, tadpoles, dragonflies, serpents and rainbirds. Other Zuni potters have since visited other storerooms of ancient Zuni pottery and brought drawings of those shapes and designs back to the pueblo, too.
About Figures and Figurines
Generally, "Figure" denotes a real or mythic creature, like an owl or human or katsina or Corn Maiden. Whether form or decoration, all Puebloan pottery figures are meant to invoke particular spiritual essences. That's why "effigy" is used almost as often as "figure" to denote these pieces.
Among most Puebloans, the figure of an owl, for example, signifies all the physical and spiritual aspects attributed to the owl. It's a form of prayer to the spirit of "Owl" and the appropriately decorated physical form is meant to make that spirit manifest. However, to the Zuni people an owl is a good omen and to the Tewa people, an owl is a bad omen. Some potters at Santa Clara have made owls anyway, they just shaped and decorated them to reflect that "badness."
That explanation may make more sense in the case of the Corn Maiden as she is a mythic entity whose existence revolves around the most ubiquitous food staple in the Puebloan world: corn (maize). All representations of the Corn Maiden are meant to invoke her benevolence and abundance for their people. Because of her mythical/spiritual nature, different pueblos have slightly different physical forms for her but they all incorporate the basic form of a female human face on an ear of corn.
The potters of Tesuque turned out thousands of muna figures (also known as rain gods)for several decades, until they virutally burned out their pottery tradition. These muna had very specific shapes but were decorated with everything from micaceous slips to incised lines to polychrome geometric designs to poster paints. They were also made purely for domestic American consumption, sometimes delivered by the barrel to be used as prizes and giveaways.
The Storyteller is another figure based on Puebloan tradition: a tribal elder singing the stories of the tribe's oral history to the children. The original was based on the traditional cultural story: a grandfather singing his part of the story in his native language so the children learn both the language and their identity against the backdrop of that history. Shortly, the storyteller form was duplicated in several other pueblos, each pueblo's potters adapting the form to their local situation. In some places, the grandmother became the primary sex of their storytellers. At Jemez, that responsibility was shared between grandmothers and grandfathers. Then some potters in search of new niches in the marketplace branched into making "spirit figure" storytellers, like eagles, ravens, hummingbirds, cats and dogs. Some Zuni potters have made storyteller owls.
Similar to the Storyteller is the Story Time: a set of separate children displayed around a larger central singing figure.
The Nativity set (also known as nacimiento) is a set of figures based on the intersection of Puebloan mythologies and stories they heard from Christian missionaries. Those potters who make them also tend to favor dress, shapes and designs that reflect their own heritage(s). The first few nativities made at Tesuque Pueblo were decorated with Spanish colonial costumes but that soon changed and every nativity made since has a distinct blend of Native American and Christian, with no other reference to colonialism. The "Singing Angel" (a single standing figure with outstretched wings and hands clasped together in prayer) and "Flight to Egypt" (usually depicting Mary with a baby Jesus on the back of a donkey and a standing Joseph nearby holding the rein) are similar mixes of tribal and Christian figures. The miniature nativities made by Santa Clara/Dineh artist Linda Askan clearly show Dineh religious influence in the headresses worn by Joseph, the angel and the three wise men. At the same time, the Dineh Folk Art nativities made by Jonathan Chee are based on the realities of daily Dineh life: the three wise men wear wide-brim hats and blue jeans, and bring gifts of salt and 50-pound bags of flour.
Pueblo and Dineh artists also make a full zoo of domesticated, farm and wild animal figures: horses, donkeys, cows, chickens, pigs, sheep, turkeys, giraffes, elephants, dogs, cats, mermaids, women-dressed-up-and-taking-selfies and cowboys among them.
About the Deer-With-Heart-Line Design
The "deer-with-heart-line" pattern may have been developed by the potters of ancient Hawikuh. We don't know, but whenever it was developed, a Zuni Pueblo potter known as We'Wha taught it to Arroh-ah-och of Laguna Pueblo in the 1890s and Arroh-ah-och took it back to Laguna and painted it there.
Some potters at Acoma Pueblo were painting the image of a deer in the 1880s but no one painted the deer-with-heart-line design until Lucy Lewis asked for and received permission from the Pueblo of Zuni. Some members of her family have been painting it since but the design hasn't spread through the community like it has through Zuni.
The "heart line" has multiple meanings: it's a prayer of thanks for good health and abundance for the spirit of the deer and good hunting for the hunter.
When the "deer-with-heart-line" pattern appears under the center of a rainbow with mountain and forest symbols on either side, that is "deer-in-his-house," a prayer for abundance and prosperity for all in the environment.
Zuni Pueblo Teaching Tree
Disclaimer: This "teaching tree" is a best effort on our part to determine who the potters are in this group and arrange them in a generational order.
The pottery tradition at Zuni Pueblo almost died out until Daisy Hooee (granddaughter of Nampeyo of Hano, Hopi-Tewa) took on the job of teaching pottery at Zuni High School in 1960. She was recruited for the job by Catalina Zunie, a Zuni potter who had spent several years just trying to get pottery on the school curriculum. Daisy also spent a year working with Catalina to become a consummate Zuni potter herself before she started teaching.
There have been several teachers at Zuni High since then and for some students, learning from their parents (who were former Zuni High students) has helped to strengthen the tradition. This diagram is subject to change should we get better info.
- Daisy Hooee Nampeyo taught 1960-1974
- Jennie Laate taught 1974-1990
- Carlos Laate
- Agnes Peynetsa
- Anderson Peynetsa & Avelia Peynetsa
- Anderson Jamie Peynetsa
- Ashley Peynetsa
- Dominic Laweka
- Priscilla Peynetsa & Daryl Westika
- Daria Westika
- Gaylon Westika
- Caylon Westika
- Brian Tsethlikai and Yvonne Nashboo
- Eileen Yatsattie






